An ice bath bowl is a simple and cost-effective method for blanching, rapidly cooling vegetables after boiling to preserve texture and color. A blast chiller offers precise temperature control and faster cooling times, making it ideal for large batches or professional kitchens where food safety standards are critical. While an ice bath is suitable for home use, a blast chiller enhances efficiency and consistency in blanching processes.
Table of Comparison
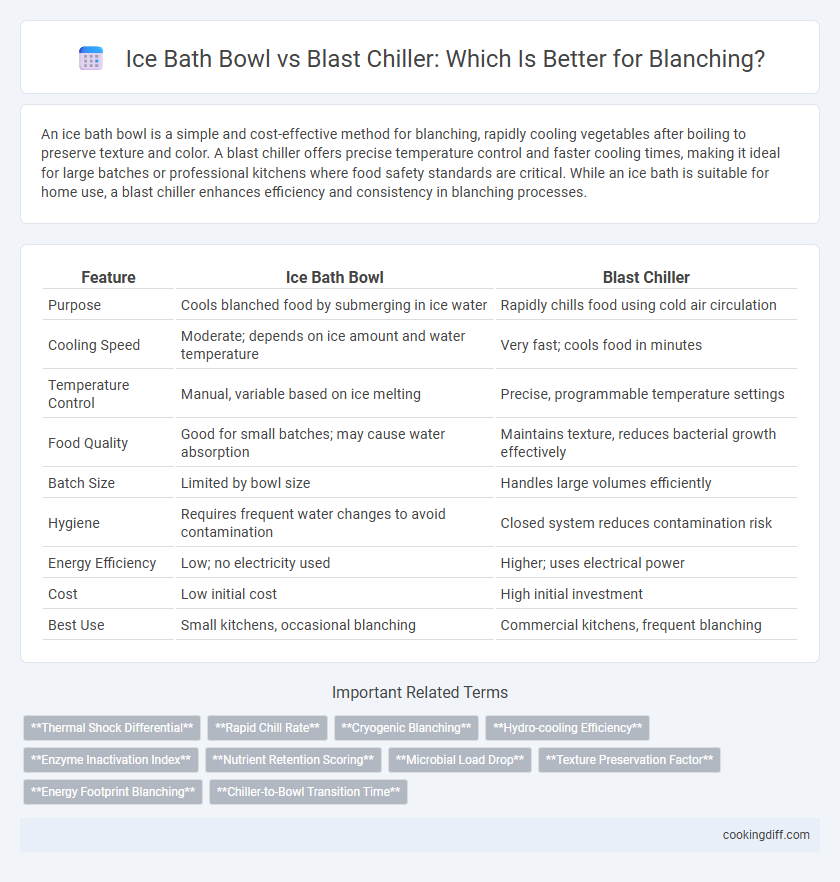
| Feature | Ice Bath Bowl | Blast Chiller |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Cools blanched food by submerging in ice water | Rapidly chills food using cold air circulation |
| Cooling Speed | Moderate; depends on ice amount and water temperature | Very fast; cools food in minutes |
| Temperature Control | Manual, variable based on ice melting | Precise, programmable temperature settings |
| Food Quality | Good for small batches; may cause water absorption | Maintains texture, reduces bacterial growth effectively |
| Batch Size | Limited by bowl size | Handles large volumes efficiently |
| Hygiene | Requires frequent water changes to avoid contamination | Closed system reduces contamination risk |
| Energy Efficiency | Low; no electricity used | Higher; uses electrical power |
| Cost | Low initial cost | High initial investment |
| Best Use | Small kitchens, occasional blanching | Commercial kitchens, frequent blanching |
Introduction to Blanching: Why Cooling Matters
Blanching is a cooking process where vegetables are briefly boiled and then rapidly cooled to halt enzymatic activity and preserve texture. Efficient cooling is critical to prevent overcooking and maintain quality during blanching.
- Ice bath bowl - Uses cold water and ice to rapidly lower the temperature of blanched vegetables, offering a simple and cost-effective cooling method.
- Blast chiller - Employs powerful refrigerated air to quickly cool foods, achieving more uniform and faster temperature reduction compared to ice baths.
- Cooling efficiency - Proper cooling minimizes nutrient loss and color degradation, essential for maintaining the sensory and nutritional quality of blanched products.
Ice Bath Bowl vs Blast Chiller: Overview
Ice bath bowls and blast chillers are both common methods used to rapidly cool blanched vegetables, ensuring texture and color retention. Choosing the appropriate cooling method impacts food safety and nutrient preservation.
- Ice Bath Bowl - Uses cold water and ice to quickly lower the temperature of blanched produce in a simple, manual setup.
- Blast Chiller - Employs powerful refrigeration to rapidly drop temperatures, offering precise control and consistency in cooling.
- Efficiency Comparison - Blast chillers cool more uniformly and faster than ice baths, reducing the risk of bacterial growth during temperature transition.
How Ice Bath Bowls Work for Blanching
Ice bath bowls rapidly cool blanched vegetables by immersing them in ice water, halting the cooking process to preserve texture and color. The cold temperature in the ice bath prevents overcooking and maintains the nutritional quality of the food.
This method is simple, cost-effective, and ideal for small batches, ensuring consistent results without specialized equipment. Ice bath bowls provide precise temperature control critical for effective blanching in home kitchens or small-scale operations.
The Blast Chiller Method Explained
The blast chiller method rapidly reduces the temperature of blanched vegetables, preserving color, texture, and nutritional value more effectively than an ice bath bowl. Unlike ice baths that rely on melting ice and slower temperature decrease, blast chillers use powerful refrigeration to cool food uniformly within minutes. This controlled cooling process minimizes bacterial growth and extends the shelf life of blanched produce in commercial kitchens.
Comparing Cooling Efficiency: Ice Bath vs Blast Chiller
Ice bath bowls cool blanched vegetables by rapidly lowering their temperature through direct ice water immersion, effectively halting the cooking process and preserving texture. This method relies on manual monitoring and can result in uneven cooling if not carefully stirred.
Blast chillers use powerful cold air circulation to uniformly and quickly reduce the temperature of blanched produce, minimizing bacterial growth and preserving quality. They offer consistent cooling efficiency and are ideal for high-volume or commercial blanching operations where precise temperature control is critical.
Impact on Food Quality and Texture
| Ice Bath Bowl | Rapidly cools blanched food, preserving crispness and vibrant color by halting cooking instantly; however, uneven cooling can cause texture inconsistencies and potential nutrient loss through water absorption. |
| Blast Chiller | Ensures uniform and rapid cooling with controlled airflow, maintaining optimal food texture and minimizing moisture loss; superior for preserving structural integrity and extending shelf life compared to ice baths. |
Time and Energy Consumption Analysis
An ice bath bowl rapidly cools blanched vegetables by immersion, consuming minimal energy but requiring manual handling and longer cooling times compared to mechanical options. A blast chiller uses forced cold air to drastically reduce cooling time, improving food safety and quality while using more electrical energy. Time efficiency of a blast chiller surpasses an ice bath, with cooling cycles reduced from 10-15 minutes to 2-5 minutes, balancing energy usage against operational speed in professional kitchens.
Space and Equipment Requirements
Ice bath bowls require minimal space and basic equipment, making them suitable for small kitchens with limited room. Blast chillers demand significant space and specialized machinery to rapidly cool large volumes efficiently.
- Ice Bath Bowl - Occupies compact counter space and involves simple, portable containers.
- Blast Chiller - Requires dedicated installation space and robust refrigeration units.
- Space Efficiency - Ice bath is ideal for limited spaces, while blast chillers need ample area to operate effectively.
Choosing between ice baths and blast chillers depends on available kitchen space and the volume of blanching required.
Cost Considerations for Home and Professional Use
Ice bath bowls offer a low-cost, accessible option for blanching in home kitchens, requiring minimal investment compared to blast chillers. However, blast chillers entail significant upfront costs but provide rapid cooling that enhances food safety and quality in professional settings.
For home use, ice bath bowls minimize expenses with reusable materials and no electricity consumption, ideal for occasional blanching tasks. Professional kitchens benefit from blast chillers despite their higher initial cost, as they reduce labor time and preserve nutritional value more effectively during high-volume food preparation. Considering the scale and frequency of blanching activities is crucial when choosing between these methods to balance cost with operational efficiency.
Related Important Terms
Thermal Shock Differential
An ice bath bowl provides immediate thermal shock by rapidly cooling blanched vegetables, preserving color and texture through a sharp temperature differential typically around 0degC, while a blast chiller offers controlled, gradual cooling that reduces temperature more evenly but with less intense thermal shock. The stark thermal shock from an ice bath bowl halts cooking instantly, whereas blast chillers minimize moisture loss and cellular damage through steady temperature reduction.
Rapid Chill Rate
An ice bath bowl provides rapid cooling by immediately lowering the temperature of blanched vegetables through direct contact with ice water, effectively halting the cooking process and preserving texture and color. In contrast, a blast chiller offers a faster, more uniform rapid chill rate by circulating cold air at high velocity, reducing the risk of bacterial growth and maintaining optimal food safety standards.
Cryogenic Blanching
Cryogenic blanching utilizes blast chillers to rapidly cool vegetables after blanching, preserving color, texture, and nutrients more effectively than traditional ice bath bowls that often lead to uneven cooling and waterlogging. The integration of cryogenic gases in blast chillers ensures immediate temperature reduction, reducing enzymatic activity and microbial growth more efficiently than ice baths.
Hydro-cooling Efficiency
Ice bath bowls provide immediate and localized hydro-cooling post-blanching by rapidly reducing food temperature through direct ice water contact, ensuring efficient heat extraction in small batches. Blast chillers, however, offer superior hydro-cooling efficiency for large-scale blanching by circulating chilled air at high velocity, delivering consistent and rapid cooling while minimizing water usage and preserving food texture.
Enzyme Inactivation Index
Ice bath bowls provide rapid cooling after blanching but often result in a higher Enzyme Inactivation Index due to slower temperature reduction, which can allow residual enzymatic activity. Blast chillers achieve a faster temperature drop, significantly lowering the Enzyme Inactivation Index and ensuring more effective enzyme inactivation for superior food quality and shelf life.
Nutrient Retention Scoring
An ice bath bowl scores lower in nutrient retention due to slower cooling rates, causing prolonged enzyme activity and vitamin degradation after blanching. Blast chillers rapidly reduce temperature, preserving maximum nutrients by halting enzymatic processes swiftly, resulting in significantly higher nutrient retention scores.
Microbial Load Drop
An ice bath bowl rapidly cools blanched vegetables, moderately reducing microbial load by halting cooking and slowing bacterial growth, but achieves less consistent temperature control compared to a blast chiller. Blast chillers provide precise, rapid cooling to temperatures below 3degC within 90 minutes, significantly enhancing microbial load reduction and prolonging shelf life by minimizing bacterial proliferation after blanching.
Texture Preservation Factor
Ice bath bowls rapidly halt the cooking process after blanching, preserving crisp texture by quickly cooling the food, although temperature consistency may vary. Blast chillers offer more uniform and controlled cooling temperatures that enhance texture preservation by preventing over-softening and maintaining firmness.
Energy Footprint Blanching
An ice bath bowl for blanching consumes minimal energy as it relies primarily on the thermal mass of ice to rapidly cool vegetables, making it an energy-efficient choice for small-scale or batch processes. In contrast, a blast chiller uses electrically powered refrigeration systems with higher energy demands but provides faster and more consistent cooling, which can reduce overall processing time and potential energy waste in large-scale blanching operations.
Ice bath bowl vs Blast chiller for Blanching. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com