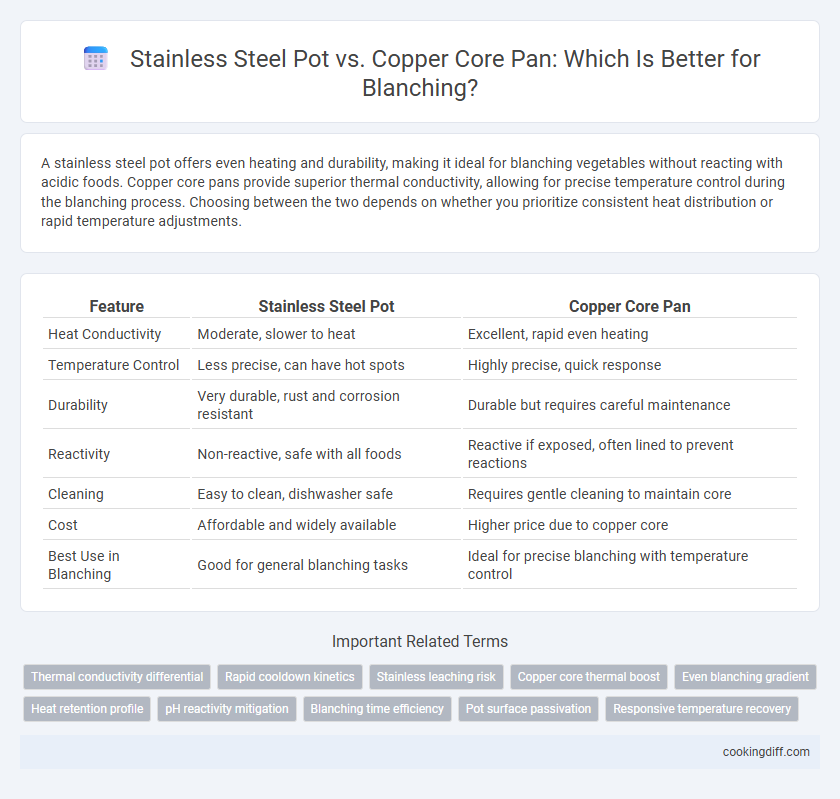
A stainless steel pot offers even heating and durability, making it ideal for blanching vegetables without reacting with acidic foods. Copper core pans provide superior thermal conductivity, allowing for precise temperature control during the blanching process. Choosing between the two depends on whether you prioritize consistent heat distribution or rapid temperature adjustments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stainless Steel Pot | Copper Core Pan |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Conductivity | Moderate, slower to heat | Excellent, rapid even heating |
| Temperature Control | Less precise, can have hot spots | Highly precise, quick response |
| Durability | Very durable, rust and corrosion resistant | Durable but requires careful maintenance |
| Reactivity | Non-reactive, safe with all foods | Reactive if exposed, often lined to prevent reactions |
| Cleaning | Easy to clean, dishwasher safe | Requires gentle cleaning to maintain core |
| Cost | Affordable and widely available | Higher price due to copper core |
| Best Use in Blanching | Good for general blanching tasks | Ideal for precise blanching with temperature control |
Introduction: Comparing Stainless Steel Pot and Copper Core Pan for Blanching
Blanching requires precise temperature control to preserve the texture and color of vegetables. Stainless steel pots provide even heat distribution with durability, but copper core pans offer superior thermal conductivity for rapid, consistent temperature changes. Choosing the right cookware impacts blanching efficiency and the quality of the final product.
Material Composition: Stainless Steel vs Copper Core
Stainless steel pots offer durability and resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for frequent blanching tasks without reacting with acidic foods. Copper core pans provide superior heat conductivity, allowing for precise temperature control and even blanching results. The combination of stainless steel and copper in copper core pans enhances performance by delivering rapid heat response while maintaining the non-reactive surface of stainless steel.
Heat Conductivity: Efficiency in Blanching
Stainless steel pots have lower heat conductivity compared to copper core pans, resulting in slower and less uniform heat distribution during blanching. Copper core pans provide rapid and even heat transfer, which is essential for maintaining the temperature needed to quickly blanch vegetables.
Copper core pans ensure more efficient heat conductivity, reducing blanching time and preserving vegetable texture and color better than stainless steel pots. The superior thermal responsiveness of copper allows for precise temperature control, preventing overcooking or undercooking during blanching. Stainless steel pots, while durable, often require more energy to maintain consistent blanching temperatures due to their lower thermal efficiency.
Durability and Longevity in Repeated Blanching
Stainless steel pots offer exceptional durability with resistance to rust, corrosion, and high heat, making them ideal for repeated blanching without warping or degradation. Their robust construction ensures consistent performance over many years, even with frequent exposure to boiling water.
Copper core pans excel in heat conductivity but require careful maintenance to prevent tarnishing and damage over time, which can affect their longevity during repeated blanching. While copper cores provide precise temperature control, their softer metal composition may lead to quicker wear compared to sturdy stainless steel pots.
Reactivity with Food and Blanching Safety
Stainless steel pots are non-reactive, ensuring that blanching acidic vegetables does not alter the flavor or cause harmful chemical reactions. Copper core pans, while excellent conductors of heat, can react with acidic foods if the lining is damaged, potentially affecting food safety during blanching.
- Stainless steel non-reactivity - This property prevents metallic taste transfer and maintains the integrity of blanched foods.
- Copper core reactivity risk - Exposure of copper to acidic foods can lead to leaching, which may pose health concerns.
- Blanching safety consideration - Choosing non-reactive cookware like stainless steel enhances food safety when blanching diverse vegetables.
Temperature Control and Precision
Stainless steel pots offer durability but have slower heat distribution, which can affect precise temperature control during blanching. Copper core pans provide superior thermal conductivity, allowing for rapid and uniform temperature adjustments essential for effective blanching.
- Heat conduction - Copper core pans conduct heat faster and more evenly than stainless steel pots, ensuring consistent blanching temperatures.
- Temperature responsiveness - Copper reacts quickly to temperature changes, preventing overheating or undercooking of vegetables.
- Durability - Stainless steel pots resist corrosion and scratches better but compromise finesse in temperature precision.
Copper core pans are preferred for blanching when exact temperature control and timing are critical to preserve color and texture.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Which cookware requires less maintenance and easier cleaning for blanching, stainless steel pots or copper core pans? Stainless steel pots are highly durable and resist stains, making them simpler to clean with standard detergents and minimal upkeep. Copper core pans demand more careful handling to prevent tarnish and often require specialized cleaners to maintain their appearance and performance.
Cost Comparison: Investment and Value
| Type of Cookware | Initial Investment | Durability and Maintenance | Overall Value for Blanching |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel Pot | Moderate cost, typically $40-$100 | Highly durable, low maintenance, resists corrosion | Cost-effective for frequent blanching tasks; offers longevity and easy cleaning |
| Copper Core Pan | High cost, usually $150-$400 | Requires careful maintenance to prevent tarnish, excellent heat conduction | Higher upfront cost but provides superior temperature control for precision blanching |
Best Use Cases: When to Choose Each Option
Stainless steel pots are ideal for blanching vegetables due to their excellent heat retention and durability, ensuring even cooking without reacting with acidic ingredients. They work best when you need a reliable, low-maintenance option for frequent blanching tasks in home cooking or commercial kitchens.
Copper core pans offer superior heat conductivity, allowing precise temperature control crucial for delicate blanching processes that require rapid temperature changes. Choose copper core for professional chefs or enthusiasts who need optimal heat responsiveness to preserve color and texture in vegetables.
Related Important Terms
Thermal conductivity differential
Copper core pans exhibit significantly higher thermal conductivity, approximately 400 W/m*K, compared to stainless steel pots, which range around 16 W/m*K, enabling faster and more even heat transfer during blanching. This superior thermal conductivity minimizes temperature fluctuations, ensuring consistent blanching results and preserving the texture and color of vegetables more effectively.
Rapid cooldown kinetics
Copper core pans offer superior thermal conductivity, enabling rapid cooldown kinetics essential for effective blanching by quickly halting the cooking process and preserving vegetable texture and color. Stainless steel pots have slower heat transfer, resulting in delayed cooldown and increased risk of overcooking during blanching.
Stainless leaching risk
Using a stainless steel pot for blanching poses a potential risk of metal leaching, especially if the cookware is scratched or exposed to acidic foods, releasing trace amounts of nickel and chromium into the food. In contrast, copper core pans, while offering superior heat conductivity and even cooking, typically have a stainless steel lining that minimizes leaching risks.
Copper core thermal boost
Copper core pans provide superior thermal conductivity compared to stainless steel pots, ensuring rapid and even heat distribution during blanching. This thermal boost minimizes cooking time, preserves vegetable texture, and enhances nutrient retention effectively.
Even blanching gradient
A copper core pan provides superior thermal conductivity, ensuring an even blanching gradient by distributing heat quickly and uniformly across the surface. Stainless steel pots, with lower heat conductivity, may result in uneven blanching as heat concentrates unevenly, leading to inconsistent texture and color in vegetables.
Heat retention profile
Copper core pans offer superior heat retention and rapid temperature responsiveness during blanching compared to stainless steel pots, which tend to lose heat more quickly due to lower thermal conductivity. This enhanced heat retention in copper core pans ensures consistent water temperature, promoting even blanching and preventing temperature fluctuations that can affect vegetable texture and color.
pH reactivity mitigation
Stainless steel pots provide superior resistance to pH reactivity during blanching, preventing metallic taste or discoloration when cooking acidic vegetables. Copper core pans, while excellent for heat conductivity, require careful monitoring as their reactive surface can interact with acidic foods unless lined with stainless steel to mitigate pH-related reactions.
Blanching time efficiency
Stainless steel pots provide consistent heat distribution but generally require longer blanching times due to slower thermal conductivity compared to copper core pans. Copper core pans significantly reduce blanching time by rapidly reaching and maintaining higher temperatures, optimizing the efficiency of the blanching process.
Pot surface passivation
Stainless steel pots offer superior surface passivation that prevents corrosion and maintains a non-reactive, smooth surface ideal for blanching vegetables without altering their taste. Copper core pans, while excellent for heat conductivity, lack the same level of passivation, making stainless steel the preferred choice to ensure consistent blanching results and durability.
Stainless steel pot vs Copper core pan for blanching. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com