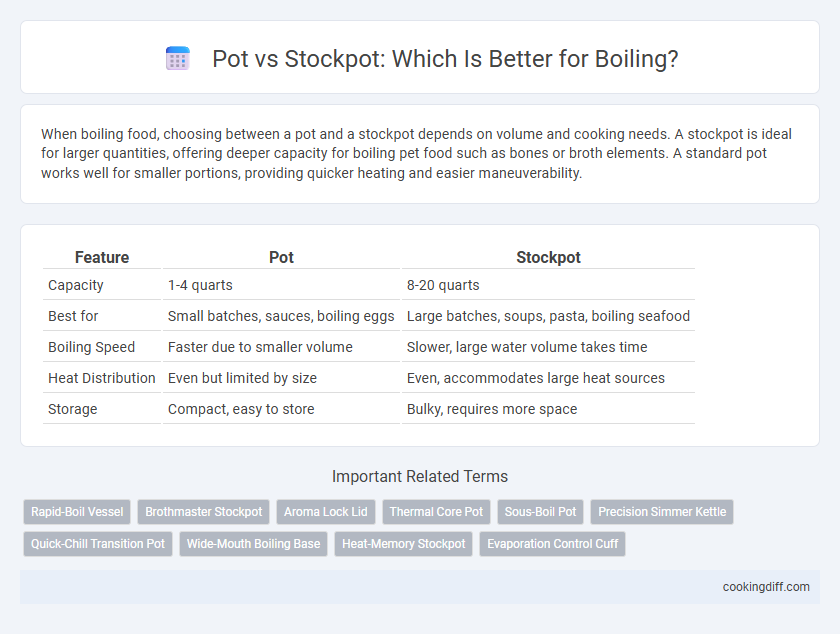
When boiling food, choosing between a pot and a stockpot depends on volume and cooking needs. A stockpot is ideal for larger quantities, offering deeper capacity for boiling pet food such as bones or broth elements. A standard pot works well for smaller portions, providing quicker heating and easier maneuverability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pot | Stockpot |
|---|---|---|
| Capacity | 1-4 quarts | 8-20 quarts |
| Best for | Small batches, sauces, boiling eggs | Large batches, soups, pasta, boiling seafood |
| Boiling Speed | Faster due to smaller volume | Slower, large water volume takes time |
| Heat Distribution | Even but limited by size | Even, accommodates large heat sources |
| Storage | Compact, easy to store | Bulky, requires more space |
Pot vs Stockpot: Understanding the Basics
A standard pot typically holds between 2 to 6 quarts, making it ideal for boiling smaller quantities of water or cooking individual portions. Stockpots generally range from 8 to 20 quarts, offering ample space to boil large batches of soup, pasta, or seafood without overflow. Choosing between a pot and a stockpot depends on the volume of boiling you require and the type of food being prepared.
Key Design Differences Between Pots and Stockpots
| Feature | Pot | Stockpot |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Typically 1 to 4 quarts, suitable for smaller quantities. | Large capacity, often 8 to 20 quarts, ideal for boiling large volumes of liquid. |
| Shape | Shorter and wider with sloped sides for quick boiling and easy stirring. | Tall and narrow with straight sides to minimize evaporation during long boiling processes. |
| Material Thickness | Moderate thickness for rapid heat conduction. | Thicker bottom for even heat distribution and to prevent scorching in large batches. |
| Handles | Usually two small side handles for easy maneuverability. | Robust, large handles designed for lifting heavy contents safely. |
Boiling Capacity: Pot or Stockpot?
Which provides a greater boiling capacity: a pot or a stockpot? Stockpots typically offer a larger volume, allowing for more water or ingredients to be boiled simultaneously. Their tall, wide design enhances heat distribution, making them ideal for preparing large batches of soups, pasta, or stocks efficiently.
Heat Distribution Comparison: Pot vs Stockpot
Stockpots offer superior heat distribution due to their wider base and thicker walls, ensuring even boiling without hotspots. Regular pots may have uneven heat transfer, leading to inconsistent boiling and potential burning at the bottom.
- Stockpots have a larger surface area - Promotes uniform heat dispersion across the entire base.
- Thicker walls on stockpots - Retain and distribute heat more efficiently during boiling.
- Regular pots often have thinner walls - Resulting in quicker hot spots and less consistent boiling temperatures.
Best Uses for Pots in Boiling
Standard pots are ideal for boiling small to medium quantities of water, making them perfect for cooking pasta, boiling eggs, or preparing vegetables. Stockpots feature a larger volume capacity, designed for boiling larger batches, such as soups, stocks, and seafood boils.
- Standard Pot for Quick Boiling - Smaller size and faster heating make standard pots efficient for everyday boiling tasks involving limited liquid amounts.
- Stockpot for Large Batches - High capacity and tall sides allow stockpots to accommodate large volumes without spillage during prolonged boiling.
- Heat Distribution - Stockpots offer better heat circulation in large quantities, ensuring even boiling and consistent cooking results.
Stockpots: The Ideal Choice for Large Batches
Stockpots offer ample capacity and even heat distribution, making them perfect for boiling large batches of food. Their tall, wide design prevents water from evaporating too quickly, ensuring consistent boiling temperatures.
- Large Capacity - Stockpots can hold several gallons of liquid, ideal for soups, stews, and pasta.
- Efficient Heat Distribution - Thick bases and stainless steel or aluminum materials provide uniform heat for thorough boiling.
- Reduced Evaporation - Tall sides minimize water loss, maintaining liquid levels longer during extended boiling sessions.
Choosing a stockpot enhances boiling efficiency and is essential for cooking large quantities accurately.
Material Matters: What’s Best for Boiling?
Stainless steel pots excel in boiling due to their durability and resistance to corrosion, ensuring even heat distribution without reacting with acidic foods. Aluminum pots heat quickly and are lightweight but may require anodizing to prevent metal leaching during prolonged boiling. Cast iron stockpots retain heat well but are less practical for boiling due to their weight and slower response to temperature changes.
Cleaning and Maintenance: Pots vs Stockpots
Cleaning a standard pot is often easier due to its smaller size and simpler design, which allows for quick rinsing and scrubbing. Stockpots, with their larger capacity and deeper structure, may require more effort and time to thoroughly clean, especially after boiling thick or starchy liquids.
Maintaining pots involves regular descaling and checking for scratches or dents that affect heat distribution. Stockpots require attention to material quality, such as stainless steel or aluminum, to prevent corrosion and ensure longevity. Proper drying and storage methods are essential to avoid rust and maintain both pots and stockpots in optimal condition.
Budget Considerations: Cost-Effectiveness
Standard pots generally cost less than stockpots, offering a budget-friendly option for everyday boiling tasks. Their smaller size and simpler design make them ideal for quick meals without a significant investment.
Stockpots provide better cost-effectiveness in the long run when preparing larger quantities or batch cooking, reducing the need for multiple smaller pots. Their durability and versatility justify a slightly higher initial price for frequent use.
Related Important Terms
Rapid-Boil Vessel
A stockpot's larger capacity and taller sides facilitate rapid boil by evenly distributing heat and minimizing water evaporation, making it ideal for boiling large quantities of liquid. In contrast, a regular pot heats smaller amounts faster but offers less surface area, resulting in slower boil times for volume cooking.
Brothmaster Stockpot
The Brothmaster Stockpot offers superior heat distribution and a larger capacity compared to a regular pot, making it ideal for boiling large quantities of broth or stock efficiently. Its heavy-gauge stainless steel construction ensures even simmering and prevents scorching, enhancing the overall cooking performance during extended boiling sessions.
Aroma Lock Lid
A stockpot with an Aroma Lock Lid enhances boiling by sealing in steam and flavors more effectively than a standard pot, ensuring rich, concentrated aromas throughout cooking. This lid design minimizes evaporation and locks in nutrients, making it ideal for soups, stocks, and broths where flavor preservation is crucial.
Thermal Core Pot
Thermal Core pots excel in boiling efficiency due to their thick, multi-layered base that ensures rapid and even heat distribution, making them ideal for both standard pots and large stockpots. Their advanced thermal technology reduces energy consumption and prevents hotspots, resulting in consistent boiling performance for soups, stocks, and other liquids.
Sous-Boil Pot
The Sous-Boil pot features a narrow base and tall sides, designed to efficiently concentrate heat for rapid boiling while minimizing evaporation compared to traditional stockpots. Its specialized shape allows even heat distribution, making it ideal for precise boiling tasks such as sous-vide preparation or delicate sauce reduction.
Precision Simmer Kettle
The Precision Simmer Kettle offers superior heat distribution and an exact temperature control ideal for boiling, outperforming standard pots and stockpots in efficiency and consistency. Its design minimizes hot spots and allows for precise simmering, making it perfect for delicate boiling tasks where accuracy is critical.
Quick-Chill Transition Pot
A Quick-Chill Transition Pot is designed for rapid temperature changes, making it ideal for boiling tasks that require immediate cooling afterward, unlike traditional stockpots which are bulkier and retain heat longer. Its efficient heat conduction and compact size provide faster boil times and quicker cooldown, enhancing kitchen workflow and energy savings.
Wide-Mouth Boiling Base
A wide-mouth boiling base in pots and stockpots enhances heat distribution and allows larger volumes of water to boil quickly, increasing efficiency for cooking tasks such as blanching or preparing broth. Stockpots typically feature broader bases compared to standard pots, optimizing surface area contact with the heat source to maintain consistent boiling temperatures for extended periods.
Heat-Memory Stockpot
Heat-memory stockpots excel in boiling by maintaining consistent temperatures for longer periods compared to regular pots, ensuring even heat distribution and efficient cooking. Their thicker construction retains heat better, reducing energy consumption and improving the quality of boiled ingredients.
Pot vs Stockpot for boiling. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com