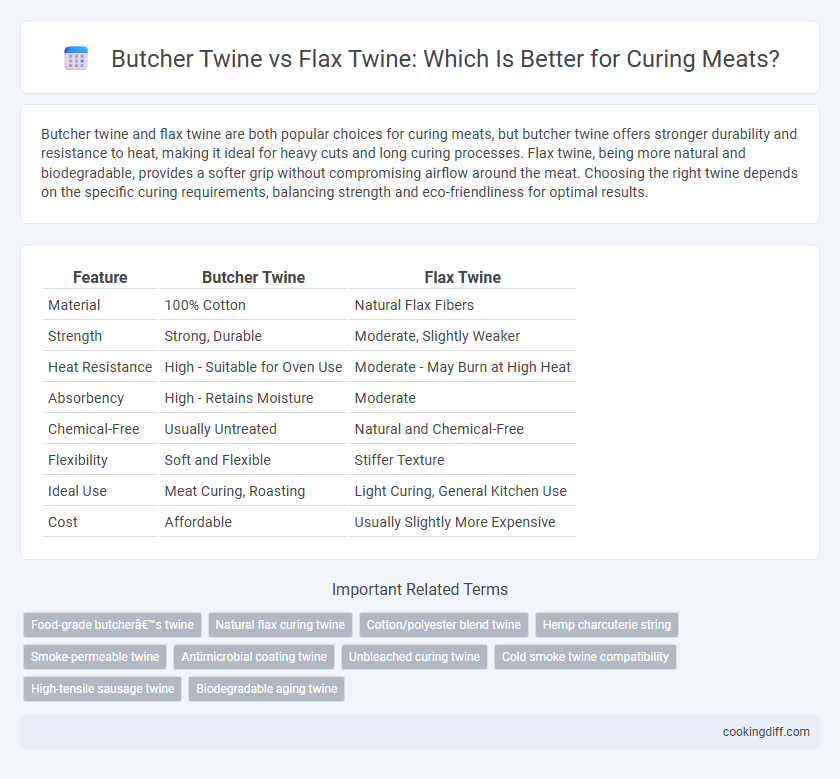
Butcher twine and flax twine are both popular choices for curing meats, but butcher twine offers stronger durability and resistance to heat, making it ideal for heavy cuts and long curing processes. Flax twine, being more natural and biodegradable, provides a softer grip without compromising airflow around the meat. Choosing the right twine depends on the specific curing requirements, balancing strength and eco-friendliness for optimal results.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Butcher Twine | Flax Twine |
|---|---|---|
| Material | 100% Cotton | Natural Flax Fibers |
| Strength | Strong, Durable | Moderate, Slightly Weaker |
| Heat Resistance | High - Suitable for Oven Use | Moderate - May Burn at High Heat |
| Absorbency | High - Retains Moisture | Moderate |
| Chemical-Free | Usually Untreated | Natural and Chemical-Free |
| Flexibility | Soft and Flexible | Stiffer Texture |
| Ideal Use | Meat Curing, Roasting | Light Curing, General Kitchen Use |
| Cost | Affordable | Usually Slightly More Expensive |
Introduction to Twine in Meat Curing
Butcher twine and flax twine are essential tools in meat curing, used primarily to secure meats during the curing process. Butcher twine is made from cotton, offering strength and heat resistance ideal for tying roasts and charcuterie.
Flax twine, derived from flax fibers, provides a natural, biodegradable alternative with a slightly rougher texture for improved grip. Both types of twine ensure even curing by maintaining the shape and integrity of the meat throughout the process.
What is Butcher Twine?
Butcher twine is a strong, food-grade cotton string specifically designed for tying meat during the curing process. It withstands high temperatures without breaking or imparting unwanted flavors, making it ideal for securing roasts, hams, and other cured meats.
Unlike flax twine, which is made from natural plant fibers and can be less durable, butcher twine provides consistent strength and safety for culinary applications. Its smooth texture ensures even pressure on the meat, promoting uniform curing and cooking.
What is Flax Twine?
Flax twine is a natural fiber twine made from the flax plant, known for its strength and biodegradability. It is often chosen over synthetic materials for curing meat, as it provides a durable yet eco-friendly option that won't impart unwanted flavors.
- Natural Composition - Flax twine is derived from flax fibers, making it an environmentally sustainable choice for food-related uses.
- Durability - Its strong fibers resist breaking, providing reliable support during the curing process of meats and sausages.
- Flavor Neutrality - Unlike some synthetic twines, flax twine does not affect the taste or aroma of cured products.
Material Composition: Butcher Twine vs Flax Twine
| Twine Type | Material Composition | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Butcher Twine | 100% cotton fibers | Food-safe, strong, heat resistant, ideal for tying meats during curing |
| Flax Twine | Natural flax fibers (linen) | Durable, biodegradable, slightly rough texture, suitable for curing but less elastic than cotton |
Strength and Durability Comparison
Butcher twine is known for its superior strength and high tensile durability, making it ideal for securing heavy cuts of meat during curing. Flax twine, while biodegradable and environmentally friendly, tends to have less tensile strength and may degrade faster under prolonged exposure to moisture and salt.
- Butcher twine exhibits higher tensile strength - It retains integrity under heavy strain, preventing breakage during extended curing processes.
- Flax twine offers natural biodegradability - This reduces environmental impact but compromises long-term durability in moist conditions.
- Durability varies with curing environments - Butcher twine performs better in humid, salty curing settings due to its synthetic composition.
Food Safety and Purity Considerations
Butcher twine, typically made from bleached cotton, offers food-safe properties with minimal chemical treatments, making it ideal for curing meats without introducing harmful contaminants. Flax twine, derived from natural flax fibers, is biodegradable and free from synthetic dyes or additives, ensuring purification and safety during prolonged curing processes. Both materials must be certified food-grade to guarantee compliance with safety standards and prevent bacterial contamination during curing.
Performance in Wet and Dry Curing Environments
Butcher twine, made from cotton, excels in wet curing environments due to its absorbency and strength, preventing breakage while holding meat securely. Flax twine, derived from flax fibers, performs better in dry curing by maintaining shape and resisting moisture-related deterioration.
In wet curing, butcher twine's ability to absorb moisture enhances flexibility and durability, making it ideal for brining and wet aging. Flax twine resists mildew and rot in dry conditions, preserving the integrity of cured meats during longer curing periods. Choosing twine based on curing method optimizes meat quality and processing efficiency.
Impact on Flavor and Cure Quality
Butcher twine and flax twine each uniquely influence the flavor and quality of cured meats due to their material properties and interaction with curing agents. Butcher twine is food-safe and neutral, preserving the original taste, while flax twine can impart subtle, earthy flavors that enhance the curing profile.
- Butcher twine is made of cotton - It resists absorbing curing liquids, maintaining consistent flavor without contamination.
- Flax twine is biodegradable and natural - It absorbs some curing agents, subtly influencing the meat's flavor complexity during curing.
- Flax twine's texture affects cure quality - Its slightly rough surface ensures secure binding, promoting uniform curing and moisture retention.
Choosing between butcher and flax twine directly impacts the sensory qualities and effectiveness of the meat curing process.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Which twine offers better cost efficiency and availability for curing purposes? Butcher twine is generally more affordable and widely available in grocery stores and butcher shops, making it a popular choice for home curing projects. Flax twine, while slightly more expensive, can be found in craft and specialty stores, offering a natural fiber alternative that some prefer despite its higher cost and limited availability.
Related Important Terms
Food-grade butcher’s twine
Food-grade butcher's twine is preferred over flax twine for curing due to its strong, food-safe cotton fibers that resist shredding and impart no flavor to meats. Butcher twine's durable, non-toxic qualities ensure secure ties and consistent drying, essential for optimal curing results.
Natural flax curing twine
Natural flax curing twine offers superior breathability and strength compared to butcher twine, making it ideal for preserving the texture and flavor of cured meats. Its biodegradable and chemical-free properties ensure a safer, more environmentally friendly curing process while maintaining durability during long-term hanging.
Cotton/polyester blend twine
Cotton/polyester blend twine offers superior durability and resistance to moisture compared to traditional butcher twine or flax twine, making it ideal for curing processes that require strong, long-lasting ties. Its synthetic fibers combined with natural cotton ensure minimal stretch and enhanced strength, supporting consistent pressure and shape retention throughout curing.
Hemp charcuterie string
Hemp charcuterie string offers superior breathability and durability compared to traditional butcher twine and flax twine, making it ideal for curing meats by allowing optimal air circulation and moisture control. Its natural antimicrobial properties help prevent mold growth, ensuring a safer and more effective curing process.
Smoke-permeable twine
Butcher twine and flax twine differ notably in smoke permeability, with butcher twine typically made from cotton offering superior breathability suitable for curing meats and allowing smoke to penetrate evenly. Flax twine, being more tightly woven and less porous, can hinder smoke absorption during the curing process, making butcher twine the preferred choice for optimal smoke flavor infusion.
Antimicrobial coating twine
Butcher twine with antimicrobial coating inhibits bacterial growth during curing, ensuring meat safety and extended shelf life. Flax twine lacks such antimicrobial properties, making butcher twine a superior choice for hygienic curing processes.
Unbleached curing twine
Unbleached curing twine, whether butcher twine or flax twine, offers strong, food-safe options essential for securing meats during curing processes, with butcher twine typically made from 100% cotton providing reliable strength and flexibility. Flax twine, composed of natural flax fibers, offers a biodegradable alternative with excellent breathability and resistance to moisture, enhancing air circulation vital for proper curing and flavor development.
Cold smoke twine compatibility
Butcher twine, made from cotton, is heat-resistant and strong, making it suitable for cold smoking as it can withstand low temperatures without imparting unwanted flavors. Flax twine, being natural and biodegradable, is less heat-resistant but still compatible with cold smoke curing, offering a more eco-friendly option that may absorb smoke flavors differently.
High-tensile sausage twine
High-tensile sausage twine, often made from flax, provides superior strength and elasticity compared to traditional butcher twine, ensuring secure, tight curing of meats without snapping. Flax twine's natural fibers resist moisture and heat, making it ideal for long curing processes, while butcher twine generally lacks the durability and tensile strength required for rigorous sausage curing.
Butcher twine vs flax twine for curing. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com