A plastic tub offers affordability and lightweight convenience for curing pets but lacks the natural breathability and weight of a fermentation crock, which provides superior moisture control and consistent temperature regulation essential for optimal curing. Fermentation crocks, typically made of ceramic, prevent unwanted air exposure and promote an ideal environment for beneficial microbial activity during the curing process. Choosing between a plastic tub and a fermentation crock impacts the quality and safety of the cured product due to differences in durability, hygiene, and fermentation control.
Table of Comparison
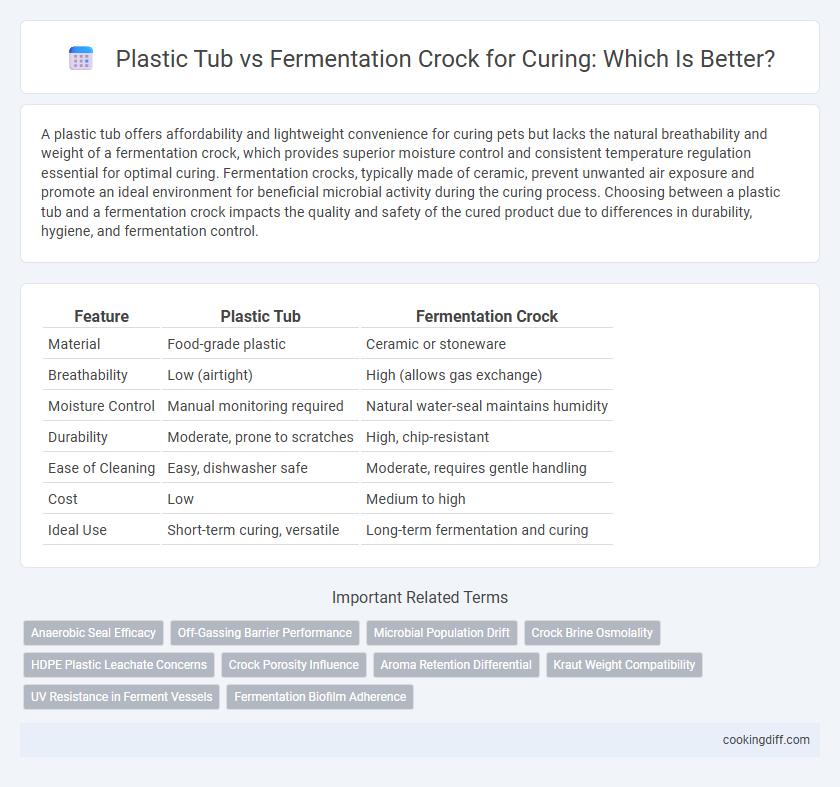
| Feature | Plastic Tub | Fermentation Crock |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Food-grade plastic | Ceramic or stoneware |
| Breathability | Low (airtight) | High (allows gas exchange) |
| Moisture Control | Manual monitoring required | Natural water-seal maintains humidity |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to scratches | High, chip-resistant |
| Ease of Cleaning | Easy, dishwasher safe | Moderate, requires gentle handling |
| Cost | Low | Medium to high |
| Ideal Use | Short-term curing, versatile | Long-term fermentation and curing |
Introduction: Importance of Choosing the Right Container for Curing
Choosing the right container is crucial for effective curing, as it directly impacts the flavor development and safety of the cured product. Plastic tubs and fermentation crocks each offer distinct advantages and challenges in the curing process.
- Plastic tubs provide versatility - They are lightweight, affordable, and easy to clean, suitable for larger batches or beginners.
- Fermentation crocks promote controlled fermentation - Designed with water-sealed lids, they create an anaerobic environment that prevents spoilage and enhances flavor complexity.
- Material impacts curing environment - Ceramic crocks offer natural insulation and durability, while plastic tubs may be prone to retain odors or allow oxygen exposure if not properly sealed.
Overview: Plastic Tub vs Fermentation Crock
Which is better for curing: a plastic tub or a fermentation crock? Plastic tubs offer lightweight durability and easier cleaning, making them ideal for beginners and small batches. Fermentation crocks, made from ceramic, provide superior air-tight environments that enhance flavor development and reduce contamination risk during long curing processes.
Material Composition and Safety Considerations
Plastic tubs used for curing are typically made from food-grade polyethylene, which is lightweight, inexpensive, and resistant to corrosion but may retain odors and stains over time. Fermentation crocks are usually crafted from ceramic or stoneware with a non-reactive glazed interior, providing a natural, breathable environment that helps maintain consistent humidity levels and prevents contamination. Safety considerations favor ceramic crocks due to their inert surfaces that do not leach chemicals, while plastic tubs require careful selection of BPA-free, durable materials to avoid potential health risks during prolonged food contact.
Fermentation Environment: Airflow and Moisture Control
Fermentation crocks provide superior airflow and moisture control due to their built-in water-seal design, which creates an anaerobic environment essential for optimal curing. Plastic tubs often lack this precise moisture regulation and can allow unwanted air exposure, increasing the risk of spoilage. Maintaining consistent humidity and limiting oxygen exposure in fermentation crocks ensures better flavor development and safe fermentation outcomes.
Ease of Use and Handling
Plastic tubs are lightweight and easy to handle, making them convenient for frequent use during the curing process. Their stackable design allows for efficient storage and easy transportation compared to heavier fermentation crocks.
Fermentation crocks, typically made of ceramic or stoneware, offer more durability but can be cumbersome due to their weight and fragility. They require careful handling to avoid chipping or cracking while cleaning or moving. Their airtight lids create an ideal environment for curing but may demand more effort during setup and maintenance.
Cleaning and Maintenance Requirements
Plastic tubs require frequent cleaning with mild detergents to prevent bacterial buildup, but their lightweight nature makes maintenance simpler. Fermentation crocks demand careful handwashing and regular inspection of the water seal to ensure proper fermentation and prevent mold growth.
- Plastic tubs are easy to scrub - Non-porous surfaces reduce residue retention, allowing quick cleanup.
- Fermentation crocks need water seal maintenance - The seal must be filled and cleaned to avoid contamination during curing.
- Both containers benefit from thorough drying - Proper drying prevents moisture-related issues such as mold and mildew proliferation.
Impact on Flavor and Fermentation Quality
Plastic tubs are more affordable and lightweight but may leach chemicals that subtly alter the flavor profile during fermentation. Fermentation crocks, made from ceramic or stoneware, provide a stable environment that enhances flavor complexity and fermentation consistency due to their breathability and natural material properties.
- Plastic tubs can affect acidity - Chemicals in some plastics interact with fermenting foods, impacting acidity and taste.
- Fermentation crocks promote even fermentation - Porous materials allow gases to escape while retaining moisture, optimizing bacterial activity.
- Flavor development is richer in crocks - Natural materials contribute to deeper, more nuanced flavor profiles over time.
Choosing fermentation crocks over plastic tubs yields superior flavor and higher fermentation quality by fostering an ideal microbial environment.
Durability and Longevity
Plastic tubs used for curing are lightweight and resistant to cracking, but they may degrade faster over time due to exposure to acidic fermenting agents and temperature fluctuations. Fermentation crocks, typically made from glazed ceramic, offer superior durability and maintain structural integrity for many years under consistent curing conditions.
Longevity is a key advantage of fermentation crocks, as they resist stains and odors while providing a stable environment ideal for long-term curing processes. Plastic tubs may require replacement more frequently, impacting overall cost efficiency and reliability in preserving food quality during extended fermentation.
Cost Comparison: Upfront and Long-Term
| Item | Upfront Cost | Long-Term Cost | Durability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plastic Tub | $15-$40 | Moderate, may require replacement every 3-5 years due to warping or odor retention | Lower durability; prone to scratches and stains |
| Fermentation Crock | $80-$200 | Low, highly durable with potential to last decades if properly maintained | High durability; made from ceramic or stoneware resistant to bacteria and odors |
Related Important Terms
Anaerobic Seal Efficacy
Fermentation crocks provide superior anaerobic seal efficacy through their water-lock designs, which prevent oxygen ingress and ensure optimal anaerobic conditions for effective curing. Plastic tubs often lack airtight seals, increasing the risk of oxidation and spoilage during the curing process.
Off-Gassing Barrier Performance
Fermentation crocks made of ceramic provide superior off-gassing barrier performance compared to plastic tubs, effectively trapping carbon dioxide while allowing excess gases to escape, which prevents spoilage. Plastic tubs often lack adequate gas permeability, increasing the risk of undesirable anaerobic conditions and off-flavors during the curing process.
Microbial Population Drift
Plastic tubs often enable greater microbial population drift due to their less porous surfaces, which can lead to inconsistent fermentation environments. Fermentation crocks, made from ceramic, provide a stable, breathable habitat that promotes a consistent and desirable microbial community crucial for effective curing.
Crock Brine Osmolality
Fermentation crocks provide superior brine osmolality control due to their non-reactive ceramic material, which maintains consistent salt concentration essential for optimal curing. In contrast, plastic tubs may leach chemicals and exhibit variable porosity, disrupting osmolality balance and compromising the curing environment.
HDPE Plastic Leachate Concerns
HDPE plastic tubs, commonly used for curing, can release trace amounts of leachates under prolonged fermentation conditions, potentially affecting food safety and flavor profiles. Fermentation crocks, typically made from ceramic or stoneware, provide a more inert curing environment, minimizing chemical leachate risks and preserving the integrity of the cured product.
Crock Porosity Influence
Fermentation crocks' porous ceramic material allows optimal airflow and moisture regulation, enhancing the curing process by preventing mold growth and promoting even salt penetration. In contrast, plastic tubs' non-porous surface can trap excess moisture, increasing the risk of spoilage and uneven curing.
Aroma Retention Differential
Plastic tubs often fail to retain the complex aromas during curing due to their non-porous surfaces that can trap moisture and promote off-smells, while fermentation crocks made from ceramic or stoneware allow for optimal airflow and micro-oxygenation, preserving and enhancing the natural aroma profiles. The porous nature of crocks facilitates consistent humidity and reduces the risk of undesirable odor development, making them superior for aroma retention in curing processes.
Kraut Weight Compatibility
Fermentation crocks typically support heavier sauerkraut weights due to their thick, durable ceramic walls that maintain consistent temperatures and prevent oxygen exposure, essential for proper fermentation. Plastic tubs, while lightweight and affordable, often lack the structural strength to handle large kraut volumes without warping, potentially compromising the weight needed for effective brine coverage and consistent curing.
UV Resistance in Ferment Vessels
Fermentation crocks made from ceramic or stoneware materials offer superior UV resistance compared to plastic tubs, preventing light-induced spoilage during the curing process. Plastic tubs often allow UV penetration, which can degrade the quality of fermenting goods and impact flavor development.
Plastic tub vs fermentation crock for curing. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com