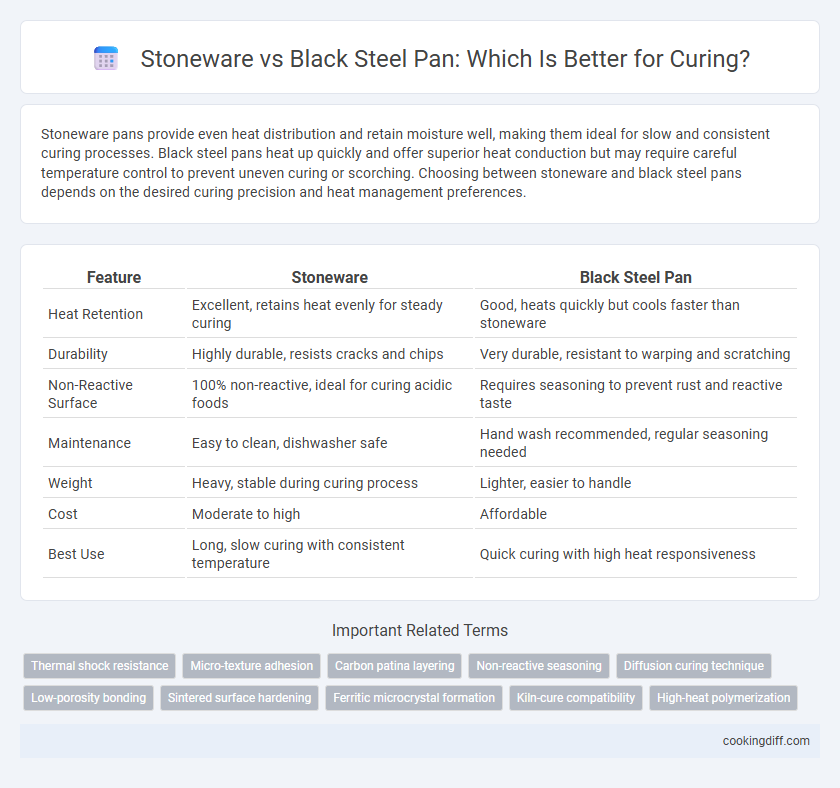
Stoneware pans provide even heat distribution and retain moisture well, making them ideal for slow and consistent curing processes. Black steel pans heat up quickly and offer superior heat conduction but may require careful temperature control to prevent uneven curing or scorching. Choosing between stoneware and black steel pans depends on the desired curing precision and heat management preferences.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stoneware | Black Steel Pan |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Retention | Excellent, retains heat evenly for steady curing | Good, heats quickly but cools faster than stoneware |
| Durability | Highly durable, resists cracks and chips | Very durable, resistant to warping and scratching |
| Non-Reactive Surface | 100% non-reactive, ideal for curing acidic foods | Requires seasoning to prevent rust and reactive taste |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, dishwasher safe | Hand wash recommended, regular seasoning needed |
| Weight | Heavy, stable during curing process | Lighter, easier to handle |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Affordable |
| Best Use | Long, slow curing with consistent temperature | Quick curing with high heat responsiveness |
Introduction to Curing: Why Pan Material Matters
| Stoneware pans offer superior heat retention and even distribution, essential for consistent curing processes in baking and cooking. |
| Black steel pans heat up quickly and provide excellent heat conduction, allowing precise temperature control during curing. |
| Choosing between stoneware and black steel pans hinges on the curing requirements--stoneware excels in slow, even heat, while black steel suits rapid temperature changes. |
Stoneware Overview: Benefits and Limitations for Curing
Stoneware offers excellent heat retention and even distribution, making it ideal for slow, consistent curing processes that require stable temperatures. Its non-porous surface prevents food absorption, ensuring flavors remain pure throughout curing.
However, stoneware is fragile and susceptible to cracking under sudden temperature changes, limiting its durability compared to black steel pans. It also takes longer to heat up and cool down, which can affect precise temperature control during curing.
Black Steel Pan Overview: Benefits and Limitations for Curing
Black steel pans offer excellent heat retention and distribution, making them effective for curing processes that require consistent temperatures. Their durability and resistance to warping under high heat enhance the curing quality compared to other materials.
However, black steel pans may require seasoning to prevent rust and maintain a non-stick surface, which can be a limitation for easy maintenance. They are also prone to reactive interactions with acidic ingredients during curing, which may affect flavor and safety.
Heat Retention and Distribution: Stoneware vs Black Steel
Stoneware offers superior heat retention, maintaining consistent temperatures ideal for slow curing processes, while black steel heats up quickly and distributes heat evenly but loses heat faster. This makes stoneware preferable for dishes requiring steady, prolonged heat, whereas black steel excels in rapid heating scenarios.
- Heat Retention Advantage - Stoneware's dense composition traps heat longer, reducing temperature fluctuations during curing.
- Efficient Heat Distribution - Black steel provides uniform heat across the surface, preventing hot spots and ensuring even cooking.
- Temperature Stability - Stoneware maintains prolonged warmth, critical for slow, thorough curing unlike black steel which cools rapidly once removed from heat.
Surface Reactivity During Curing: Key Differences
Stoneware and black steel pans exhibit distinct surface reactivities during curing that impact the flavor and texture of foods. The non-reactive surface of stoneware prevents chemical interactions, while black steel pans may alter curing outcomes due to their reactive metal composition.
- Stoneware's inert surface - prevents metal ions from leaching into food, preserving pure flavors during curing.
- Black steel's reactive surface - can catalyze oxidation reactions, subtly changing the curing process and flavor profile.
- Heat retention differences - stoneware retains heat evenly, while black steel heats quickly and unevenly, affecting curing consistency.
Choosing between stoneware and black steel pans for curing depends on desired flavor preservation and reaction effects.
Durability and Lifespan: Long-Term Performance Comparison
Which material offers superior durability and lifespan for long-term curing: stoneware or black steel pans? Stoneware provides excellent heat retention and resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for consistent curing without warping or degradation. Black steel pans, while offering rapid heating, may require more maintenance to prevent rust and can show wear faster under prolonged curing conditions.
Maintenance and Care: Cleaning and Seasoning Requirements
Stoneware requires gentle cleaning and minimal seasoning, making it low-maintenance for curing tasks. Black steel pans demand regular seasoning and thorough drying to prevent rust and maintain their non-stick surface.
- Stoneware cleaning - Easily cleaned with warm water and mild detergent, avoiding abrasive materials to preserve the surface.
- Black steel pan seasoning - Needs frequent seasoning with oil to build a protective layer that prevents rust during curing.
- Maintenance frequency - Stoneware can be cured with less frequent maintenance, while black steel pans require consistent care after each use.
Flavor Development: Impact of Pan Material on Cured Foods
Stoneware pans provide even heat distribution, which enhances the slow curing process and results in more complex flavor development in cured foods. Black steel pans, while heating quickly, can create hotspots that may unevenly cure foods, impacting flavor consistency.
The porous surface of stoneware allows for better moisture regulation, preserving natural juices and intensifying savory notes during curing. In contrast, black steel pans retain heat longer but may promote faster drying, potentially altering the delicate balance of flavors. Choosing stoneware often leads to richer, more nuanced cured products due to its gentle and stable heat retention.
Cost and Accessibility: Stoneware vs Black Steel Pan
Stoneware pans typically come at a higher cost but offer excellent heat retention and even curing, making them a long-term investment for baking enthusiasts. Black steel pans are more affordable and widely accessible, providing good heat conduction and durability for curing purposes. Both options vary in price and availability, with black steel being the preferred choice for budget-conscious users seeking reliable performance.
Related Important Terms
Thermal shock resistance
Stoneware offers superior thermal shock resistance compared to black steel pans, making it ideal for gradual temperature changes during curing processes. Black steel pans tend to warp or crack under rapid thermal fluctuations, reducing their durability and effectiveness for consistent heat retention.
Micro-texture adhesion
Stoneware offers a porous micro-texture that enhances seasoning adhesion during curing, creating a durable, non-stick surface over time. Black steel pans develop a smooth patina that promotes even polymerization but may require more frequent maintenance to maintain optimal micro-texture adhesion.
Carbon patina layering
Stoneware offers a porous surface that absorbs oils, creating a natural carbon patina over time, enhancing flavor depth and seasoning durability. Black steel pans develop a robust carbon patina through repeated heating and oiling, resulting in superior non-stick properties and long-lasting rust resistance.
Non-reactive seasoning
Stoneware excels in non-reactive seasoning due to its inert surface, preventing flavor alterations and chemical reactions during curing, while black steel pans require regular maintenance to maintain their seasoned layer and avoid rust. The porous nature of stoneware promotes even moisture distribution essential for consistent curing, whereas black steel's durability allows for high-heat applications but may introduce metallic taste if the seasoning is compromised.
Diffusion curing technique
Stoneware's porous surface allows for even heat distribution, enhancing the diffusion curing process by promoting uniform absorption and gradual moisture release. In contrast, black steel pans conduct heat rapidly, which can cause uneven curing and potential hot spots, making stoneware a superior choice for controlled diffusion curing techniques.
Low-porosity bonding
Stoneware pans offer superior low-porosity bonding compared to black steel pans, ensuring minimal absorption and enhanced durability during curing. This characteristic prevents moisture loss and preserves flavor integrity, making stoneware ideal for prolonged curing processes.
Sintered surface hardening
Stoneware pans provide a naturally sintered surface formed through high-temperature firing, resulting in enhanced surface hardening that improves durability and heat retention during curing. In contrast, black steel pans require seasoning to develop a hardened patina but lack the intrinsic surface sintering of stoneware, offering less resistance to wear and potential stickiness over time.
Ferritic microcrystal formation
Stoneware excels in promoting uniform ferritic microcrystal formation during curing due to its stable thermal conductivity, enhancing the steel's corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. In contrast, black steel pans may induce uneven microstructural development, potentially compromising the consistency and durability of the cured surface.
Kiln-cure compatibility
Stoneware offers excellent kiln-cure compatibility due to its ability to withstand high temperatures without warping or cracking, ensuring even heat distribution during the curing process. In contrast, black steel pans may experience deformation or uneven heat retention, making them less reliable for consistent kiln curing results.
Stoneware vs black steel pan for curing. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com