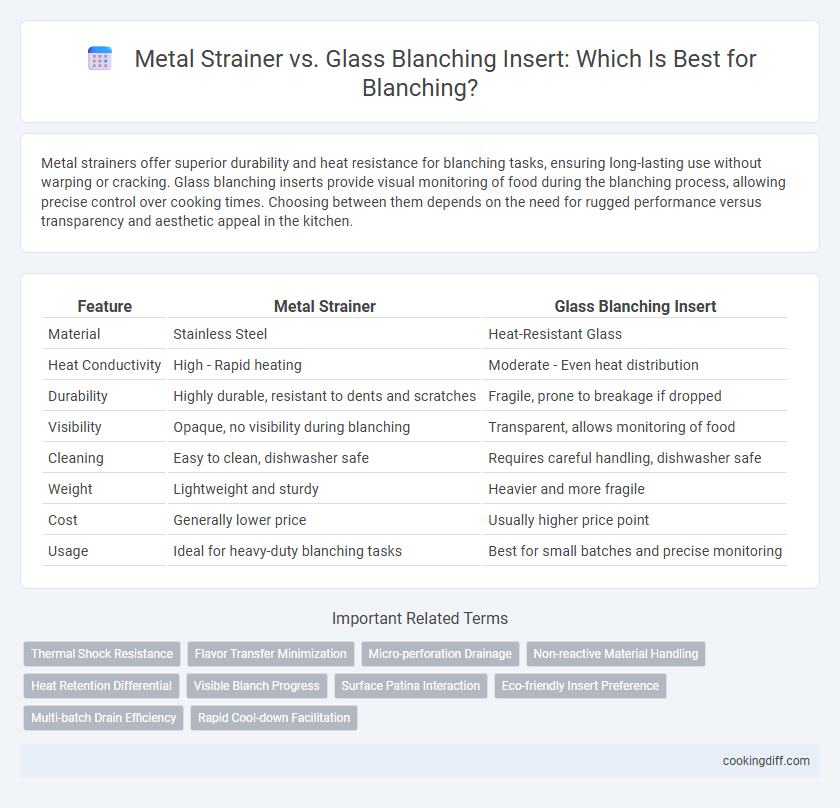
Metal strainers offer superior durability and heat resistance for blanching tasks, ensuring long-lasting use without warping or cracking. Glass blanching inserts provide visual monitoring of food during the blanching process, allowing precise control over cooking times. Choosing between them depends on the need for rugged performance versus transparency and aesthetic appeal in the kitchen.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Metal Strainer | Glass Blanching Insert |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Stainless Steel | Heat-Resistant Glass |
| Heat Conductivity | High - Rapid heating | Moderate - Even heat distribution |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to dents and scratches | Fragile, prone to breakage if dropped |
| Visibility | Opaque, no visibility during blanching | Transparent, allows monitoring of food |
| Cleaning | Easy to clean, dishwasher safe | Requires careful handling, dishwasher safe |
| Weight | Lightweight and sturdy | Heavier and more fragile |
| Cost | Generally lower price | Usually higher price point |
| Usage | Ideal for heavy-duty blanching tasks | Best for small batches and precise monitoring |
Introduction to Blanching Tools
Blanching tools like metal strainers and glass blanching inserts play a crucial role in the blanching process by allowing quick and efficient submersion and removal of vegetables from boiling water. Metal strainers offer durability and heat conductivity, ideal for high-temperature use, while glass inserts provide a non-reactive surface that prevents metallic tastes and allows easy visual monitoring. Selecting the right blanching tool enhances cooking precision and preserves the nutritional quality and color of vegetables.
Metal Strainer vs Glass Blanching Insert: An Overview
Metal strainers offer superior durability and excellent heat conduction, making them ideal for rapid blanching processes. Glass blanching inserts provide a non-reactive surface and visibility but tend to heat unevenly and can be fragile.
Metal strainers are preferred for their resistance to thermal shock and ease of cleaning, while glass inserts allow precise monitoring of food during blanching. The choice depends on the blanching method and material sensitivity. Overall, metal strainers combine practicality with efficiency, whereas glass inserts are favored for gentle processing and aesthetic appeal.
Heat Conductivity: Metal vs Glass
| Material | Heat Conductivity | Blanching Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Metal Strainer | High thermal conductivity facilitates rapid heat transfer, ensuring quicker blanching times. | Ideal for uniform heat exposure, reducing blanching duration and preserving texture and color. |
| Glass Blanching Insert | Lower thermal conductivity results in slower heat transfer, leading to extended blanching periods. | Provides gentle heat exposure but may cause uneven blanching and longer cooking times. |
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Metal strainers demonstrate superior durability due to their resistance to high temperatures and physical impact, ensuring a longer lifespan in blanching processes. Glass blanching inserts, while providing excellent heat resistance and chemical stability, are more prone to cracking or breaking under sudden thermal shocks or mechanical stress. Choosing a metal strainer often results in better longevity and consistent performance during repeated blanching cycles.
Safety Considerations in Blanching
Which is safer to use for blanching, a metal strainer or a glass blanching insert? Metal strainers offer robust heat resistance and reduce the risk of breakage during high-temperature blanching, making them a reliable option. Glass blanching inserts, while heat-resistant, pose a greater safety risk due to potential shattering under thermal shock or impact.
Ease of Handling and Usability
Metal strainers offer lightweight construction that enhances ease of handling during blanching compared to the heavier glass blanching inserts. Their heat-resistant handles provide safer maneuverability, making them more user-friendly for quick food transfers.
- Lightweight Design - Metal strainers are easier to lift and move due to their reduced weight compared to glass inserts.
- Heat Resistance - Metal handles remain cool longer, reducing the risk of burns when removing food from boiling water.
- Durability - Metal strainers are less prone to breakage under frequent use, increasing long-term usability.
Cleaning and Maintenance Differences
Metal strainers used for blanching are typically easier to clean because they withstand scrubbing and high temperatures without damage. Their non-porous surface resists staining and retains less residue compared to glass inserts.
Glass blanching inserts require more careful maintenance to avoid scratches and cracks, often needing gentle hand washing to preserve their clarity. Over time, mineral deposits and discoloration can accumulate, necessitating occasional soaking with vinegar or specialized cleaners.
Impact on Food Quality and Texture
Metal strainers conduct heat rapidly, enabling quick blanching that preserves crispness and vibrant color in vegetables. Glass blanching inserts heat more slowly, resulting in gentler cooking that may soften textures and slightly dull colors.
- Metal Strainer - Facilitates rapid heat transfer, maintaining firmness and nutrient retention in blanched foods.
- Glass Insert - Offers even heating but slower temperature adjustment, which can lead to softer textures.
- Texture Impact - Faster blanching with metal enhances snap and color, while glass may produce a milder, less crisp result.
Choosing a metal strainer typically yields better preservation of food quality and texture during blanching.
Cost Analysis: Metal vs Glass Inserts
Metal strainers typically have a lower initial cost compared to glass blanching inserts but may incur higher long-term expenses due to rusting and wear. Glass inserts, though more expensive upfront, offer better durability and resistance to corrosion, potentially reducing replacement frequency.
- Initial Purchase Price - Metal strainers are generally more affordable than glass inserts, making them cost-effective for short-term use.
- Longevity and Durability - Glass blanching inserts resist rust and chemical damage, which can lower maintenance and replacement costs over time.
- Maintenance Costs - Metal strainers may require more frequent cleaning and eventual replacement due to corrosion, increasing overall costs.
Related Important Terms
Thermal Shock Resistance
Metal strainers offer superior thermal shock resistance compared to glass blanching inserts, allowing for rapid temperature changes without cracking or breaking. This durability makes metal strainers more reliable for repeated blanching tasks involving sudden immersion in boiling water and ice baths.
Flavor Transfer Minimization
Metal strainers can sometimes impart a slight metallic taste to foods during blanching, whereas glass blanching inserts are non-reactive and effectively minimize flavor transfer, preserving the natural taste of vegetables. The inert properties of glass ensure no chemical interaction, making it ideal for maintaining purity in flavor-sensitive blanching processes.
Micro-perforation Drainage
A metal strainer with micro-perforation offers superior drainage efficiency during blanching by allowing rapid water flow and preventing vegetable loss, unlike glass blanching inserts that often have larger holes and slower drainage. The fine micro-perforations in metal strainers enhance heat transfer and ensure uniform blanching by quickly removing water and steam.
Non-reactive Material Handling
Glass blanching inserts provide superior non-reactive material handling compared to metal strainers, preventing any risk of chemical reaction or metallic taste transfer during the blanching process. The inert nature of glass ensures food safety and maintains the pure flavor of vegetables, while metal strainers, especially those made from reactive alloys, may interact with acidic or alkaline foods, compromising quality.
Heat Retention Differential
A metal strainer rapidly conducts heat away from blanching water, causing faster temperature drops, whereas a glass blanching insert retains heat longer due to its lower thermal conductivity. This heat retention differential results in more consistent blanching temperatures when using glass inserts, enhancing texture and color in vegetables.
Visible Blanch Progress
Metal strainers offer durability and excellent heat conduction, allowing for quick blanching and easy visibility of water movement but can obscure direct visual inspection of the food. Glass blanching inserts provide clear visibility of blanch progress, enabling precise timing and monitoring of color changes, although they may conduct heat less efficiently and require careful handling.
Surface Patina Interaction
Metal strainers develop a natural surface patina during blanching that can enhance flavor through mild oxidation, while glass blanching inserts maintain a neutral, non-reactive surface that prevents any alteration of food taste. The interaction between the blanching medium and the metal's surface patina influences heat distribution and can subtly affect nutrient retention compared to the inert properties of glass.
Eco-friendly Insert Preference
Metal strainers and glass blanching inserts both serve essential roles in the blanching process, but glass inserts are preferred for eco-friendly kitchens due to their non-toxic, reusable nature and resistance to corrosion, ensuring no harmful chemicals leach into food. Metal strainers, while durable and heat-conductive, often contain coatings that may degrade over time, making glass inserts a sustainable and safer alternative for environmentally conscious cooks.
Multi-batch Drain Efficiency
Metal strainers provide superior multi-batch drain efficiency during blanching due to their sturdy construction and larger perforations, which facilitate faster water drainage and prevent clogging. Glass blanching inserts, while visually appealing and non-reactive, typically feature smaller drainage holes that slow the draining process and reduce overall efficiency when handling multiple batches.
Metal Strainer vs Glass Blanching Insert for blanching. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com