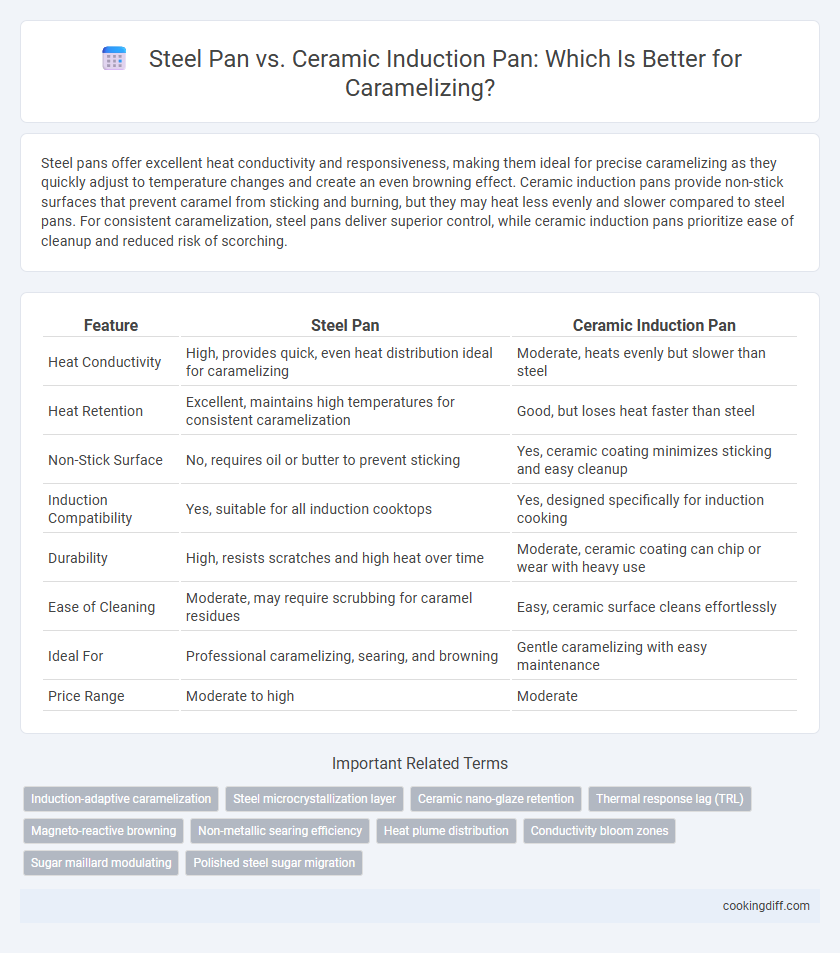
Steel pans offer excellent heat conductivity and responsiveness, making them ideal for precise caramelizing as they quickly adjust to temperature changes and create an even browning effect. Ceramic induction pans provide non-stick surfaces that prevent caramel from sticking and burning, but they may heat less evenly and slower compared to steel pans. For consistent caramelization, steel pans deliver superior control, while ceramic induction pans prioritize ease of cleanup and reduced risk of scorching.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Steel Pan | Ceramic Induction Pan |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Conductivity | High, provides quick, even heat distribution ideal for caramelizing | Moderate, heats evenly but slower than steel |
| Heat Retention | Excellent, maintains high temperatures for consistent caramelization | Good, but loses heat faster than steel |
| Non-Stick Surface | No, requires oil or butter to prevent sticking | Yes, ceramic coating minimizes sticking and easy cleanup |
| Induction Compatibility | Yes, suitable for all induction cooktops | Yes, designed specifically for induction cooking |
| Durability | High, resists scratches and high heat over time | Moderate, ceramic coating can chip or wear with heavy use |
| Ease of Cleaning | Moderate, may require scrubbing for caramel residues | Easy, ceramic surface cleans effortlessly |
| Ideal For | Professional caramelizing, searing, and browning | Gentle caramelizing with easy maintenance |
| Price Range | Moderate to high | Moderate |
Introduction: Caramelizing Techniques
Caramelizing involves heating sugar to transform its flavor and texture, requiring precise temperature control and even heat distribution. Steel pans excel in heat conductivity, enabling fast and consistent caramelization without hot spots.
Ceramic induction pans offer smooth, non-reactive surfaces that prevent sugar from sticking and burning during caramelization. Their compatibility with induction cooktops ensures efficient energy use and stable temperature maintenance critical for delicate caramelizing techniques.
Material Matters: Steel vs Ceramic Induction
Steel pans offer superior heat conductivity and high-temperature tolerance essential for even caramelization, while ceramic induction pans provide non-reactive surfaces that prevent sticking but heat more slowly. The choice between steel and ceramic impacts caramelization quality due to differences in heat distribution and surface reactivity.
- Heat Conductivity - Steel pans heat rapidly and evenly, ensuring consistent caramelization without hot spots.
- Surface Reactivity - Ceramic induction pans are non-reactive, preventing caramel from sticking or burning during cooking.
- Temperature Tolerance - Steel withstands very high temperatures critical for developing caramel's rich flavor and color.
Heat Distribution and Control
Steel pans provide superior heat conductivity, allowing for rapid and even heat distribution essential for precise caramelizing. Their responsiveness to temperature changes offers excellent control, minimizing the risk of burning sugar during the process.
Ceramic induction pans heat more slowly and may have hot spots, resulting in uneven caramelization. Although ceramic surfaces are non-reactive and easy to clean, they often lack the precise temperature control needed for perfect caramel development.
Responsiveness to Temperature Changes
| Pan Type | Responsiveness to Temperature Changes | Impact on Caramelizing |
|---|---|---|
| Steel Pan | High thermal conductivity enables rapid temperature adjustments. | Allows precise control to prevent burning and achieve even caramelization. |
| Ceramic Induction Pan | Slower response to temperature changes due to ceramic coating. | May cause uneven caramelization and increased risk of overheating sugar. |
Nonstick Properties and Caramel Release
Which pan offers better nonstick properties and easier caramel release for caramelizing, steel or ceramic induction pans? Steel pans typically provide superior heat conductivity, allowing even caramelization but often require seasoning to enhance nonstick properties. Ceramic induction pans feature a naturally nonstick surface that facilitates caramel release, reducing sticking and making cleanup simpler.
Flavor Development in Steel vs Ceramic Pans
Steel pans excel in caramelizing due to their superior heat conductivity, promoting even browning and Maillard reactions that enhance rich, complex flavors. Ceramic induction pans offer a more gentle heat, which can result in slower caramelization and a milder, less-developed flavor profile. The high responsiveness of steel pans makes them preferred for achieving deep caramel flavors quickly and efficiently.
Ease of Cleaning After Caramelizing
Steel pans often require more effort to clean after caramelizing due to sugar residue that can stick and burn onto the surface. Ceramic induction pans typically offer easier cleanup as their non-stick surfaces prevent caramel from adhering strongly.
- Steel pans retain caramel residue - The surface texture allows burnt sugar to cling, demanding thorough scrubbing.
- Ceramic induction pans have non-stick coatings - These coatings minimize sticking of caramel, facilitating gentle cleaning.
- Cleaning time varies - Ceramic pans generally reduce post-caramelizing cleanup duration compared to steel pans.
Durability and Longevity for Caramelizing
Steel pans offer superior durability for caramelizing due to their resistance to high heat and physical wear, making them long-lasting in kitchen use. Ceramic induction pans provide even heating but may suffer from chipping and reduced longevity when exposed to frequent temperature changes during caramelization.
- Steel pans resist warping - They maintain shape and performance after repeated high-heat caramelizing tasks.
- Ceramic pans are prone to cracking - Thermal shock from rapid heating can reduce their lifespan significantly.
- Steel enables consistent heat retention - This ensures uniform caramelization without degradation over time.
Choosing steel over ceramic induction pans enhances durability and longevity for caramelizing applications.
Price and Value Considerations
Steel pans generally offer a lower price point compared to ceramic induction pans, making them more accessible for budget-conscious cooks. Their durability and excellent heat conductivity provide solid value for caramelizing tasks despite the initial lower cost.
Ceramic induction pans are priced higher due to advanced materials and compatibility with induction cooktops, offering superior heat distribution and non-stick surfaces. The investment in ceramic pans can enhance caramelizing precision and reduce cleanup time, adding long-term value for frequent users. While pricier, their performance benefits may justify the cost for dedicated caramelization enthusiasts.
Related Important Terms
Induction-adaptive caramelization
Steel pans provide superior heat conduction and rapid temperature adjustment, essential for precise caramelization on induction cooktops, ensuring even browning and preventing sugar crystallization. Ceramic induction pans offer non-stick surfaces but often heat less evenly, which may result in inconsistent caramelization and require more careful temperature control.
Steel microcrystallization layer
Steel pans with a microcrystallization layer provide superior heat retention and even distribution essential for precise caramelizing, preventing hotspots that cause uneven browning. Ceramic induction pans offer non-stick benefits but often lack the durable thermal conductivity and surface resilience needed for consistent caramelization results.
Ceramic nano-glaze retention
Ceramic induction pans with nano-glaze technology offer superior caramelizing performance due to their excellent heat retention and even distribution, preventing hotspots that can cause sugar to burn. Unlike steel pans, the nano-glaze surface maintains its smooth, non-stick properties over time, ensuring consistent browning and easier cleanup.
Thermal response lag (TRL)
Steel pans exhibit a lower thermal response lag (TRL) compared to ceramic induction pans, allowing for faster temperature adjustments crucial for precise caramelizing control. Ceramic induction pans retain heat longer due to higher TRL, which can cause uneven caramelization or burning if temperature is not carefully managed.
Magneto-reactive browning
Steel pans excel in caramelizing due to their superior magneto-reactive browning properties, which enhance Maillard reactions through rapid and even heat distribution on induction cooktops. Ceramic induction pans, while providing non-stick surfaces, lack the magnetic responsiveness needed for efficient caramelization, resulting in slower browning and less flavorful outcomes.
Non-metallic searing efficiency
Steel pans offer superior non-metallic searing efficiency for caramelizing due to their excellent heat conductivity and even heat distribution, allowing sugars to caramelize quickly and evenly without sticking. Ceramic induction pans, while providing non-reactive surfaces, often have slower heat response times which can result in less consistent caramelization and increased risk of uneven browning.
Heat plume distribution
Steel pans offer rapid and even heat plume distribution, enabling precise temperature control essential for consistent caramelization, while ceramic induction pans distribute heat more slowly and less uniformly, which can lead to uneven caramelization and potential hot spots. The superior thermal conductivity of steel ensures a stable temperature environment that promotes the Maillard reaction required for rich, deep caramel flavors.
Conductivity bloom zones
Steel pans excel in reaching and maintaining high temperatures swiftly due to their superior thermal conductivity, creating ideal bloom zones for even caramelization. Ceramic induction pans provide more consistent low-to-medium heat distribution but may struggle to achieve the quick, intense heat spikes necessary for optimal caramel bloom development.
Sugar maillard modulating
Steel pans distribute heat more evenly and reach higher temperatures quickly, promoting efficient Maillard reactions and consistent sugar caramelization. Ceramic induction pans offer gentler, more controlled heat, reducing the risk of scorching while allowing slower, more precise modulation of sugar's Maillard browning process.
Steel pan vs ceramic induction pan for caramelizing. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com