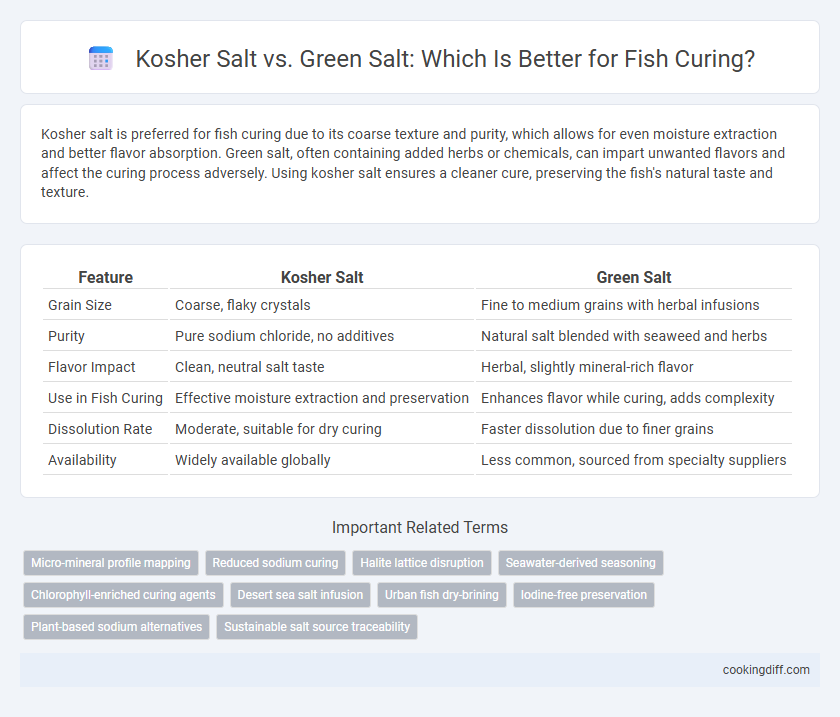
Kosher salt is preferred for fish curing due to its coarse texture and purity, which allows for even moisture extraction and better flavor absorption. Green salt, often containing added herbs or chemicals, can impart unwanted flavors and affect the curing process adversely. Using kosher salt ensures a cleaner cure, preserving the fish's natural taste and texture.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Kosher Salt | Green Salt |
|---|---|---|
| Grain Size | Coarse, flaky crystals | Fine to medium grains with herbal infusions |
| Purity | Pure sodium chloride, no additives | Natural salt blended with seaweed and herbs |
| Flavor Impact | Clean, neutral salt taste | Herbal, slightly mineral-rich flavor |
| Use in Fish Curing | Effective moisture extraction and preservation | Enhances flavor while curing, adds complexity |
| Dissolution Rate | Moderate, suitable for dry curing | Faster dissolution due to finer grains |
| Availability | Widely available globally | Less common, sourced from specialty suppliers |
Understanding Fish Curing: A Brief Overview
| Kosher salt has a coarse texture and dissolves quickly, making it ideal for evenly drawing moisture from fish during curing. Green salt, often infused with herbs or seaweed, imparts additional flavors but dissolves more slowly, affecting the curing time and taste profile. Choosing between kosher salt and green salt depends on the desired flavor intensity and curing duration in fish preservation. |
What Is Kosher Salt?
Kosher salt is a coarse-grained salt commonly used in fish curing due to its purity and ease of handling. It is free of additives, making it ideal for drawing out moisture and enhancing flavor without altering the fish's natural taste.
- Coarse grain - Large crystals make kosher salt easy to pinch and spread evenly over fish.
- Pure composition - Typically contains only sodium chloride, free from anti-caking agents or iodine.
- Moisture extraction - Efficiently draws moisture from fish, improving texture and preservation.
Kosher salt's properties make it a preferred choice over green salt for effective fish curing.
What Is Green Salt?
Green salt, also known as seaweed salt, is a natural curing agent made by infusing kosher salt with powdered seaweed, enhancing flavor and mineral content. It is prized in fish curing for its umami properties and subtle marine aroma.
- Natural Composition - Green salt combines kosher salt crystals with dehydrated seaweed, adding trace minerals like iodine and magnesium.
- Flavor Enhancement - The infusion imparts a rich, savory umami taste that complements the delicate flavor of cured fish.
- Preservation Quality - Green salt maintains moisture while effectively inhibiting bacterial growth, ensuring fish freshness during curing.
Mineral Composition: Kosher Salt vs Green Salt
Kosher salt is primarily composed of sodium chloride with minimal trace minerals, making it ideal for fish curing due to its pure salinity and clean flavor profile. Green salt, typically harvested from seaweed-infused waters, contains additional minerals such as magnesium and calcium, which can subtly enhance the taste and texture of cured fish.
The higher mineral content in green salt contributes to increased umami and complexity, beneficial for artisanal curing processes. Kosher salt's coarse texture and consistent grain size ensure even curing without introducing unwanted flavors from impurities.
Texture and Grain Size Differences
Kosher salt has larger, coarser grains that create a flaky texture ideal for drawing moisture from fish without over-salting. Green salt features finer, denser crystals that penetrate fish faster, resulting in a firmer and more uniform cure.
- Kosher Salt Grain Size - Larger crystals enhance control over curing speed and texture development.
- Green Salt Texture - Finer grains allow for quicker salt absorption and a tighter fish texture.
- Impact on Fish Cure - Grain size influences moisture extraction and final mouthfeel of cured fish.
Flavor Profiles in Fish Curing
Kosher salt, known for its coarse texture and clean, pure saltiness, enhances fish curing by drawing out moisture without overpowering the fish's natural flavors. Green salt, infused with herbs like dill and seaweed, imparts a subtle aromatic complexity that complements the delicate taste of cured fish. Selecting between kosher salt and green salt depends on the desired flavor profile, where kosher salt offers simplicity and green salt introduces a nuanced, herbal character.
Curing Efficiency: Which Salt Works Best?
Kosher salt is favored in fish curing due to its coarse texture, which allows for even moisture extraction and better control over salt absorption. Green salt, often containing added minerals or herbs, can impart unique flavors but may not cure as uniformly as kosher salt. Studies show kosher salt's larger crystals dissolve slowly, enhancing curing efficiency and preserving fish texture more effectively than green salt.
Nutritional Impacts on Fish Curing
How do Kosher salt and Green salt differ in their nutritional impacts on fish curing? Kosher salt, known for its purity and larger grain size, typically contains no additives, ensuring a cleaner curing process without altering the fish's natural mineral content. Green salt, often infused with seaweed or herbs, can introduce additional minerals such as iodine and antioxidants, potentially enhancing the nutritional profile of cured fish.
Cost and Availability Comparison
Kosher salt is widely available in most supermarkets and specialty stores, making it a cost-effective option for fish curing. Its large grain size and purity contribute to consistent curing results without a significant price difference compared to other salts.
Green salt, often sourced from specific regions or produced with unique mineral content, tends to be less readily available and more expensive. The limited supply and artisanal production methods increase its cost, making it a premium choice for curing fish.
Related Important Terms
Micro-mineral profile mapping
Kosher salt contains larger, coarser grains predominantly composed of sodium chloride with minimal trace minerals, making it ideal for extracting moisture without altering flavor profiles in fish curing. Green salt, enriched with a diverse micro-mineral profile including magnesium, calcium, and potassium, enhances the curing process by contributing to improved texture and subtle mineral complexity in cured fish.
Reduced sodium curing
Kosher salt is preferred for fish curing due to its coarse texture and purity, allowing for better control over sodium levels and reduced salt absorption compared to green salt, which often contains added minerals that can increase sodium content. Reduced sodium curing with kosher salt enhances flavor while maintaining the fish's moisture and texture, making it a healthier option for preserving seafood.
Halite lattice disruption
Kosher salt's larger, irregular crystals disrupt the halite lattice more effectively than green salt, enhancing moisture extraction during fish curing. This structural difference accelerates osmosis, resulting in a firmer texture and improved preservation quality.
Seawater-derived seasoning
Kosher salt, favored for fish curing due to its coarse texture and pure sodium chloride content, effectively draws out moisture while preserving the fish's natural flavor. Green salt, derived from seawater and enriched with marine minerals and algae, offers a complex umami profile and enhanced mineral absorption, making it ideal for creating a distinctive cured fish product.
Chlorophyll-enriched curing agents
Chlorophyll-enriched curing agents like green salt offer antioxidant properties and natural antimicrobial effects that enhance fish preservation compared to traditional kosher salt, which primarily provides texture and moisture control. The presence of chlorophyll in green salt improves color retention and extends shelf life by reducing oxidative spoilage in cured fish products.
Desert sea salt infusion
Desert sea salt infusion, rich in minerals and trace elements, enhances the curing process by intensifying flavor profiles and improving moisture retention in fish compared to traditional kosher salt. Green salt, while valued for its herbal-infused qualities, lacks the mineral density found in Desert sea salt, making it less effective in achieving optimal preservation and taste during fish curing.
Urban fish dry-brining
Kosher salt's coarse texture and pure sodium chloride content enable even moisture extraction and enhanced flavor absorption in urban fish dry-brining, while green salt, infused with herbs and seaweed, imparts unique botanical flavors and minerals that enrich the curing process. Optimizing curing times with Kosher salt ensures firm texture and preservation, whereas green salt offers a nuanced taste profile ideal for artisanal urban fish curing recipes.
Iodine-free preservation
Kosher salt is preferred for fish curing due to its coarse texture and lack of additives, enabling even moisture extraction and flavor enhancement without iodine contamination. Green salt, often containing iodine, can alter the fish's natural taste and is less ideal for preservation methods requiring iodine-free curing to maintain purity and quality.
Plant-based sodium alternatives
Kosher salt, widely used in fish curing for its large, coarse grains that promote even moisture extraction, contrasts with green salt, a plant-based sodium alternative derived from seaweed and herbs, offering a natural umami flavor and lower sodium content. Green salt enhances preservation with antioxidant properties and minerals, making it a sustainable option in traditional curing processes where reduced sodium intake is desired.
Kosher Salt vs Green Salt for fish curing. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com