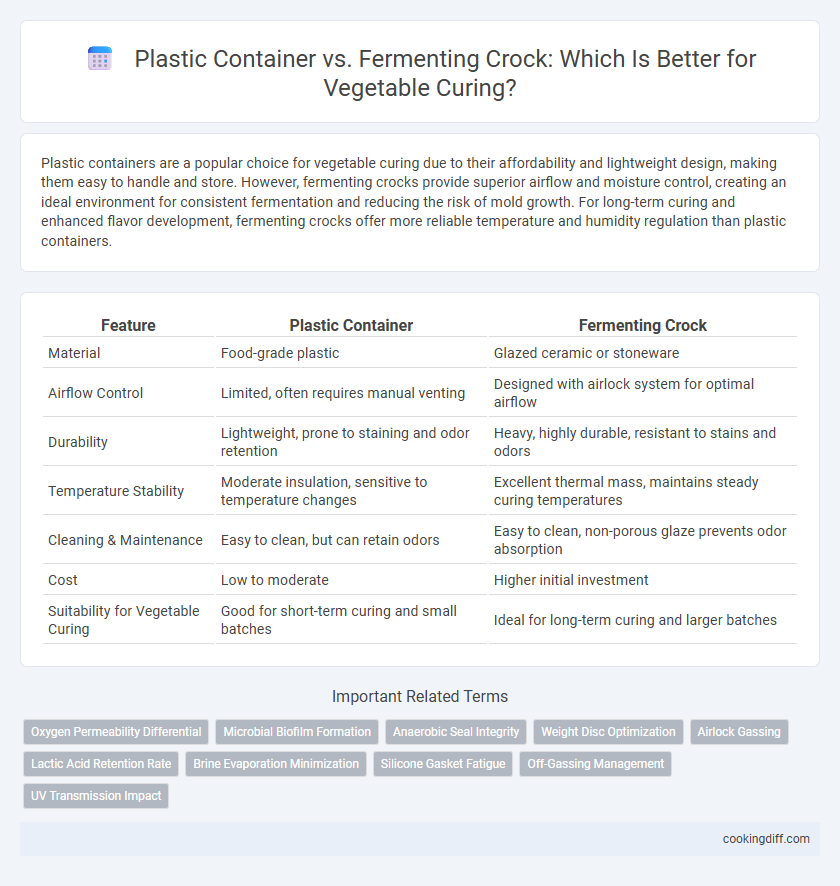
Plastic containers are a popular choice for vegetable curing due to their affordability and lightweight design, making them easy to handle and store. However, fermenting crocks provide superior airflow and moisture control, creating an ideal environment for consistent fermentation and reducing the risk of mold growth. For long-term curing and enhanced flavor development, fermenting crocks offer more reliable temperature and humidity regulation than plastic containers.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plastic Container | Fermenting Crock |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Food-grade plastic | Glazed ceramic or stoneware |
| Airflow Control | Limited, often requires manual venting | Designed with airlock system for optimal airflow |
| Durability | Lightweight, prone to staining and odor retention | Heavy, highly durable, resistant to stains and odors |
| Temperature Stability | Moderate insulation, sensitive to temperature changes | Excellent thermal mass, maintains steady curing temperatures |
| Cleaning & Maintenance | Easy to clean, but can retain odors | Easy to clean, non-porous glaze prevents odor absorption |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Higher initial investment |
| Suitability for Vegetable Curing | Good for short-term curing and small batches | Ideal for long-term curing and larger batches |
Introduction to Vegetable Curing Methods
| Plastic containers offer convenience and affordability for vegetable curing, featuring lightweight design and easy cleanup, which is ideal for beginners or small batches. |
| Fermenting crocks provide traditional curing methods with ceramic material that maintains optimal anaerobic conditions and consistent temperature control, essential for high-quality fermentation. |
| Choosing between plastic containers and fermenting crocks depends on factors such as fermentation duration, batch size, and desired flavor profile in vegetable curing processes. |
What is a Plastic Container for Curing?
A plastic container for curing is a durable, lightweight vessel designed to hold vegetables during the fermentation process. It provides a non-reactive environment that helps maintain consistent temperatures and moisture levels essential for proper fermentation.
- Non-reactive material - Plastic containers resist corrosion and prevent chemical reactions with acidic fermented vegetables.
- Lightweight and portable - These containers are easy to handle and store compared to heavier ceramic fermenting crocks.
- Sealable lids - Many plastic containers come with airtight lids that help control oxygen exposure and reduce contamination risks.
Plastic containers offer a practical and economical option for vegetable curing, especially for beginners and small-batch fermenters.
What is a Fermenting Crock?
A fermenting crock is a specialized ceramic vessel designed to create an anaerobic environment ideal for vegetable fermentation. It features a water-sealed airlock system that prevents oxygen from entering while allowing gases to escape, ensuring optimal lactic acid fermentation.
- Material Composition - Made of non-porous ceramic that maintains consistent temperature and inhibits harmful bacteria growth.
- Water-Sealed Lid - Uses a moat filled with water to create an airtight seal without trapping carbon dioxide gas.
- Optimal Environment - Provides ideal anaerobic conditions promoting beneficial microbes for safe, effective vegetable curing.
Benefits of Using Plastic Containers for Vegetable Curing
Plastic containers offer excellent airtight sealing, significantly reducing the risk of contamination during vegetable curing. Their lightweight nature and durability make them easy to handle and clean, ensuring a hygienic curing environment.
Unlike fermenting crocks, plastic containers provide a more cost-effective and versatile solution for various vegetable quantities. The transparency of plastic allows for easy monitoring of the curing process without disturbing the contents.
Advantages of Fermenting Crocks in Vegetable Curing
Fermenting crocks provide an ideal environment for vegetable curing by maintaining consistent temperature and moisture levels, which prevents spoilage and enhances flavor development. Their airlock design allows gases to escape while keeping oxygen out, minimizing the risk of mold and harmful bacteria growth. The durable ceramic material of fermenting crocks also offers superior resistance to acids generated during fermentation compared to plastic containers, ensuring safer and longer-lasting curing results.
Safety Considerations: Plastic vs. Ceramic Crocks
Plastic containers used for vegetable curing should be food-grade and BPA-free to avoid chemical leaching, ensuring safe fermentation. Ceramic fermenting crocks offer a non-reactive surface that helps maintain consistent temperature and prevents contamination through their natural porous structure.
Ceramic crocks are preferred for long-term fermentation due to their durability and ability to keep out light and air, which inhibits spoilage. Plastic containers may absorb odors and stains over time, increasing the risk of bacterial growth if not properly sanitized. For optimal safety, use dedicated fermentation containers and regularly inspect them for cracks or damage.
Flavor and Texture Differences in Cured Vegetables
Plastic containers often produce a milder flavor and softer texture in cured vegetables due to limited airflow and inconsistent fermentation temperatures. Fermenting crocks, made from porous ceramic, allow for better oxygen exchange, resulting in more complex flavors and crisper textures. The material's natural thermal insulation helps maintain optimal fermentation conditions, enhancing overall vegetable quality.
Cost Comparison: Plastic Containers vs. Fermenting Crocks
Plastic containers typically offer a lower upfront cost than fermenting crocks, making them accessible for budget-conscious users. However, fermenting crocks provide long-term durability and can be more cost-effective over time despite the higher initial investment.
- Initial cost difference - Plastic containers generally range from $10 to $30, while fermenting crocks often cost between $50 and $150.
- Longevity and durability - Fermenting crocks are made of ceramic materials that resist staining and odors, increasing lifespan compared to plastic.
- Reusability - Fermenting crocks maintain structural integrity through multiple uses, reducing replacement frequency and overall expenses.
Maintenance and Cleaning: Which is Easier?
Which option requires less maintenance and easier cleaning: a plastic container or a fermenting crock for vegetable curing? Plastic containers are generally easier to clean due to their smooth, non-porous surfaces that resist staining and odor retention. Fermenting crocks, often made of ceramic, require careful hand washing and regular inspection to prevent mold growth in their crevices and airlocks.
Related Important Terms
Oxygen Permeability Differential
Plastic containers exhibit higher oxygen permeability compared to fermenting crocks, which are designed with airlock systems that minimize oxygen exposure during vegetable curing. This oxygen permeability differential significantly affects the anaerobic fermentation process, ensuring better control of lactic acid bacteria growth and preventing spoilage in fermenting crocks.
Microbial Biofilm Formation
Fermenting crocks promote beneficial microbial biofilm formation through their porous ceramic material, creating an anaerobic environment ideal for lactic acid bacteria during vegetable curing. In contrast, plastic containers often lack sufficient breathability, which can hinder optimal biofilm development and may lead to unwanted microbial growth.
Anaerobic Seal Integrity
Plastic containers offer varying anaerobic seal integrity, often relying on tight lids or additional sealing methods that may allow minimal air infiltration during vegetable curing. Fermenting crocks utilize heavy ceramic weights and water-sealed airlocks to maintain a robust anaerobic environment, minimizing oxygen exposure and promoting consistent fermentation outcomes.
Weight Disc Optimization
Plastic containers offer lightweight convenience but may require heavier weight discs to maintain proper pressure and prevent air pockets during vegetable curing. Fermenting crocks, typically made of ceramic or stoneware, provide stable weight discs designed to evenly distribute pressure, optimizing the curing environment for consistent fermentation results.
Airlock Gassing
Plastic containers without proper airlocks often allow excessive gassing escape, leading to inconsistent fermentation and potential spoilage, whereas fermenting crocks equipped with built-in airlocks maintain an anaerobic environment that controls carbon dioxide release and prevents oxygen from entering. This precise airlock gassing system enhances microbial activity, ensuring optimal vegetable curing and flavor development.
Lactic Acid Retention Rate
Plastic containers often exhibit lower lactic acid retention rates during vegetable curing due to less controlled fermentation environments compared to fermenting crocks. Fermenting crocks maintain consistent anaerobic conditions, promoting higher lactic acid preservation essential for optimal vegetable fermentation.
Brine Evaporation Minimization
Fermenting crocks excel in minimizing brine evaporation due to their heavy ceramic lids and water-sealed designs that maintain an airtight environment, preserving moisture levels crucial for vegetable curing. Plastic containers often lack these features, leading to higher brine evaporation and inconsistent fermentation results.
Silicone Gasket Fatigue
Plastic containers offer affordability and lightweight convenience but often suffer from poor silicone gasket fatigue resistance, leading to compromised airtight seals over time in vegetable curing. Fermenting crocks, typically made from ceramic with durable silicone gaskets, provide superior long-term seal integrity, ensuring consistent anaerobic conditions essential for optimal fermentation results.
Off-Gassing Management
Plastic containers often trap gases released during vegetable curing, leading to buildup of off-gassing compounds such as carbon dioxide and organic acids, which can affect flavor and fermentation quality. Fermenting crocks are designed with built-in airlocks or water-seal systems that allow controlled release of gases, ensuring optimal off-gassing management and preserving vegetable texture and taste.
Plastic Container vs Fermenting Crock for vegetable curing. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com