Drum drying produces instant soup mixes with a consistent texture and excellent solubility by evenly spreading the slurry over heated drums, which rapidly removes moisture while preserving flavor. Superheated steam drying uses high-temperature steam to efficiently dry soup mixes without oxidation, maintaining vibrant colors and nutritional quality. Compared to superheated steam drying, drum drying often results in thicker flakes ideal for quick rehydration, while superheated steam drying offers energy efficiency and minimal thermal degradation.
Table of Comparison
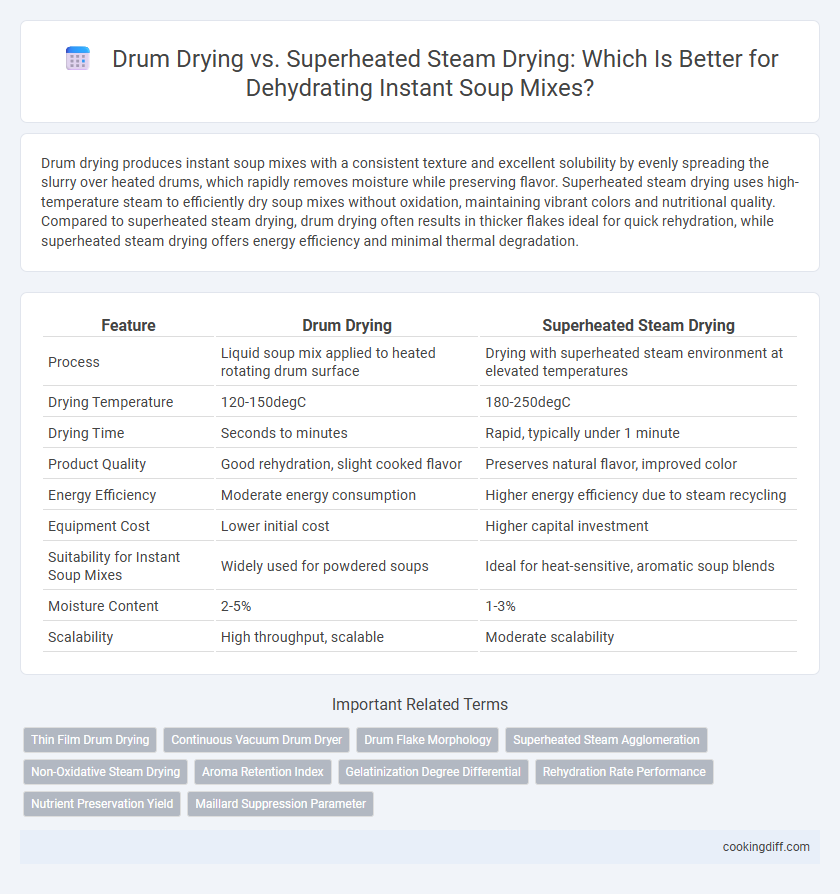
| Feature | Drum Drying | Superheated Steam Drying |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Liquid soup mix applied to heated rotating drum surface | Drying with superheated steam environment at elevated temperatures |
| Drying Temperature | 120-150degC | 180-250degC |
| Drying Time | Seconds to minutes | Rapid, typically under 1 minute |
| Product Quality | Good rehydration, slight cooked flavor | Preserves natural flavor, improved color |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate energy consumption | Higher energy efficiency due to steam recycling |
| Equipment Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher capital investment |
| Suitability for Instant Soup Mixes | Widely used for powdered soups | Ideal for heat-sensitive, aromatic soup blends |
| Moisture Content | 2-5% | 1-3% |
| Scalability | High throughput, scalable | Moderate scalability |
Introduction to Drying Techniques for Instant Soup Mixes
Drum drying and superheated steam drying are critical techniques for producing instant soup mixes, each offering unique advantages in preserving flavor and nutrients. These methods influence the texture, solubility, and shelf life of the final product, determining consumer satisfaction and market success.
- Drum Drying - Utilizes heated rotating drums to quickly evaporate moisture, creating thin flakes ideal for rehydration.
- Superheated Steam Drying - Employs steam above boiling point to dry ingredients gently, maintaining more natural flavors.
- Instant Soup Quality - Drying method directly affects the solubility rate and mouthfeel of instant soup mixes, impacting convenience and taste.
Selecting the appropriate drying technique is essential for optimizing product quality and manufacturing efficiency in instant soup production.
Overview of Drum Drying: Principles and Process
Drum drying involves spreading a liquid or puree onto the surface of a heated rotating drum, rapidly evaporating moisture to produce a dry film that is then scraped off. This method is widely used in instant soup mixes to create fine, uniform flakes that dissolve quickly in hot water.
- Heat Transfer Mechanism - Moisture is removed primarily through conduction from the hot drum surface to the food product.
- Product Texture - Results in dense, flaky particles ideal for quick rehydration in instant soups.
- Energy Efficiency - Requires less energy than superheated steam drying due to direct contact heating.
Superheated Steam Drying: Mechanism and Application
How does superheated steam drying improve the quality of instant soup mixes? Superheated steam drying uses steam at temperatures above 100degC, which facilitates rapid moisture removal without oxidation, preserving flavor and nutrients. This method is especially effective in maintaining the rehydration properties and texture of instant soup powders compared to conventional drum drying.
Comparative Analysis: Drum Drying vs Superheated Steam Drying
Drum drying offers rapid moisture removal and produces a uniform, low-moisture instant soup powder but may cause slight flavor degradation due to high surface temperatures. Superheated steam drying maintains better flavor and nutrient retention by reducing oxidation and thermal damage, although it requires more complex equipment and higher operational costs. For instant soup mixes, choosing between drum drying and superheated steam drying depends on prioritizing either processing efficiency or enhanced product quality.
Impact on Nutritional Retention in Instant Soup Mixes
Drum drying often leads to higher nutrient loss in instant soup mixes due to prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures, while superheated steam drying better preserves heat-sensitive vitamins and antioxidants. The choice of drying method directly influences the nutritional quality and consumer health benefits of the final instant soup product.
- Drum drying nutrient degradation - Extended heat exposure in drum drying causes significant reduction in vitamin C and B-complex vitamins in soup mixes.
- Superheated steam drying nutrient retention - Rapid moisture removal at lower temperatures helps retain more phytochemicals and essential micronutrients.
- Impact on antioxidant levels - Superheated steam drying preserves higher antioxidant activity compared to the oxidative degradation seen in drum drying.
Effects on Flavor, Aroma, and Color
Drum drying preserves the natural flavor and color of instant soup mixes by rapidly evaporating moisture while maintaining Maillard reaction levels, resulting in a rich aroma and deep color. Superheated steam drying uses high-temperature steam to dry without oxygen, minimizing oxidative damage and preserving volatile aroma compounds for a fresher flavor profile. Color retention is enhanced in superheated steam drying due to reduced thermal degradation, producing vibrant soup mixes with appealing sensory qualities.
Texture and Rehydration Characteristics
Drum drying produces instant soup mixes with a smooth, uniform texture due to the thin film of product dried on the heated drum surface. This method retains a good rehydration capacity, allowing the soup mix to dissolve quickly and evenly in hot water.
Superheated steam drying enhances particle porosity, resulting in a lighter texture and improved solubility for instant soup mixes. The increased rehydration rate from this technique leads to faster dispersion and better flavor release during preparation.
Energy Efficiency and Operational Costs
| Drying Method | Energy Efficiency | Operational Costs |
|---|---|---|
| Drum Drying | Lower energy efficiency due to direct contact heating and higher thermal losses. | Higher operational costs driven by energy consumption and frequent maintenance requirements. |
| Superheated Steam Drying | Improved energy efficiency achieved through reduced heat losses and better heat transfer. | Lower operational costs resulting from decreased energy usage and reduced equipment wear. |
Scalability and Industrial Suitability
Drum drying offers moderate scalability with straightforward operation, making it suitable for small to medium-sized instant soup mix production. Its lower capital investment and maintenance costs favor industrial applications with established production lines.
Superheated steam drying provides high scalability ideal for large-scale industrial operations due to its continuous processing capability. This method enhances product consistency and energy efficiency, crucial for extensive instant soup mix manufacturing. Integration with existing industrial systems improves overall productivity and reduces downtime.
Related Important Terms
Thin Film Drum Drying
Thin film drum drying offers precise heat control and rapid moisture removal, preserving the nutritional quality and flavor of instant soup mixes better than superheated steam drying. This method ensures uniform drying with minimal thermal degradation, enhancing solubility and shelf life of the final product.
Continuous Vacuum Drum Dryer
Continuous Vacuum Drum Dryers enhance instant soup mix quality by maintaining low temperatures during dehydration, preserving flavors and nutrients better than superheated steam drying. This method ensures uniform moisture removal and extended shelf life, outperforming traditional drum or superheated steam drying techniques in efficiency and product consistency.
Drum Flake Morphology
Drum drying produces irregular, porous flakes with a rough surface that enhance rapid rehydration and improved texture in instant soup mixes, while superheated steam drying yields denser, more uniform flakes with smoother morphology but slower rehydration rates. The distinct morphological differences impact solubility, particle size distribution, and overall sensory attributes critical for consumer acceptance of instant soup products.
Superheated Steam Agglomeration
Superheated steam agglomeration enhances instant soup mixes by creating uniform, porous granules that improve solubility and rehydration rates compared to traditional drum drying. This method also preserves flavor and nutrients more effectively due to the gentle, low-oxygen environment during dehydration.
Non-Oxidative Steam Drying
Drum drying uses heated drums to quickly evaporate moisture from instant soup mixes, but it risks oxidation that can degrade flavor and nutrients. Superheated steam drying offers a non-oxidative steam drying environment, preserving the color, taste, and nutritional quality by minimizing exposure to oxygen while efficiently removing moisture.
Aroma Retention Index
Drum drying achieves a higher Aroma Retention Index for instant soup mixes due to its lower drying temperature and shorter exposure time, preserving volatile aroma compounds more effectively. Superheated steam drying, while efficient in moisture removal, often results in lower aroma retention because of prolonged heat exposure that degrades delicate flavor molecules.
Gelatinization Degree Differential
Drum drying achieves higher gelatinization degrees in instant soup mixes due to direct heat transfer, promoting starch granule swelling and improved texture. Superheated steam drying results in a lower gelatinization degree, preserving some native starch structure but potentially reducing rehydration efficiency.
Rehydration Rate Performance
Drum drying produces instant soup mixes with a porous, easily rehydrated structure, resulting in faster rehydration rates compared to superheated steam drying, which can cause surface hardening and slower water absorption. The higher thermal gradient in drum drying preserves solubility and reduces clumping, optimizing instant soup mix rehydration performance.
Nutrient Preservation Yield
Drum drying preserves nutrient yield by rapidly removing moisture through heated drum surfaces, minimizing nutrient loss in instant soup mixes. Superheated steam drying enhances nutrient retention by creating an oxygen-free environment that prevents oxidative degradation, resulting in higher quality and nutrient-dense instant soup mixes.
Drum drying vs Superheated steam drying for instant soup mixes. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com