Electric dehydrators provide consistent heat and airflow, making them ideal for evenly drying fruits, vegetables, and meats during meal prep. Heat pump dehydrators use lower temperatures and recycle air, resulting in energy-efficient drying while preserving more nutrients and flavors. Choosing between the two depends on meal prep volume, energy priorities, and desired drying speed.
Table of Comparison
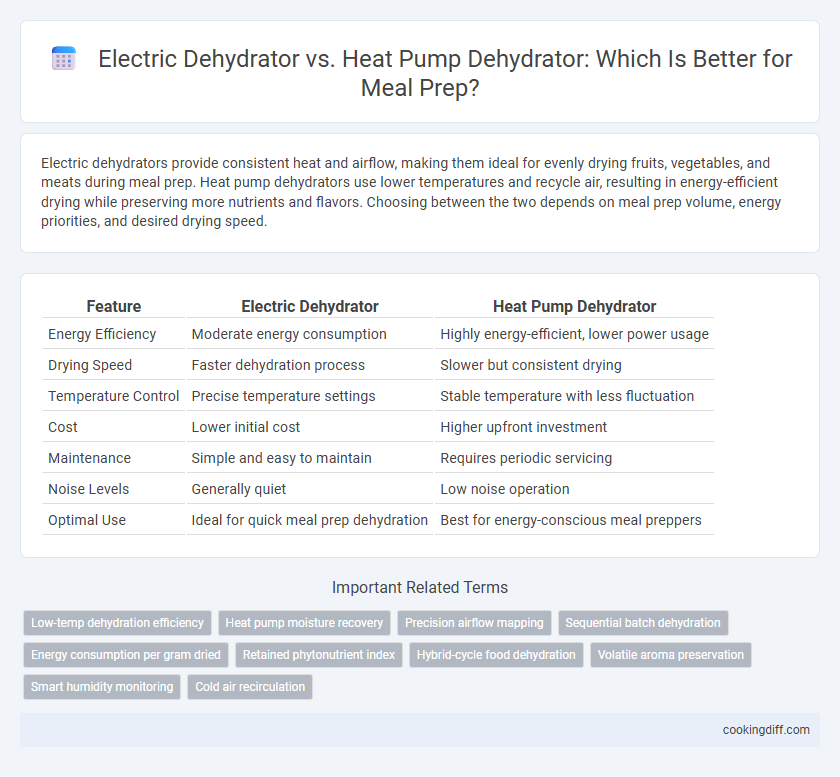
| Feature | Electric Dehydrator | Heat Pump Dehydrator |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate energy consumption | Highly energy-efficient, lower power usage |
| Drying Speed | Faster dehydration process | Slower but consistent drying |
| Temperature Control | Precise temperature settings | Stable temperature with less fluctuation |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher upfront investment |
| Maintenance | Simple and easy to maintain | Requires periodic servicing |
| Noise Levels | Generally quiet | Low noise operation |
| Optimal Use | Ideal for quick meal prep dehydration | Best for energy-conscious meal preppers |
Introduction to Food Dehydration Methods
| Dehydration Method | Energy Efficiency | Temperature Control | Suitability for Meal Prep |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Dehydrator | Moderate energy consumption, uses direct electric heat elements | Simple, adjustable temperature settings ideal for various foods | Widely used for straightforward drying tasks with consistent results |
| Heat Pump Dehydrator | High energy efficiency by recycling heat through a heat pump system | Precise temperature and humidity control enhancing food preservation | Optimal for long-duration meal prep with delicate food textures |
Overview of Electric Dehydrators
Electric dehydrators use a heating element and fan to circulate warm air evenly around food, typically operating at temperatures between 95degF to 165degF. These devices provide consistent drying performance and are suitable for various meal prep ingredients such as fruits, vegetables, and meats.
They are generally more affordable and widely available compared to heat pump dehydrators, making them a popular choice for home kitchens. The electric models consume moderate energy and offer easy temperature control, optimizing dehydration efficiency for meal preparation.
Understanding Heat Pump Dehydrators
Heat pump dehydrators use advanced refrigeration technology to remove moisture efficiently at lower temperatures, preserving nutrients and flavors in meal prep. This method consumes up to 50% less energy compared to traditional electric dehydrators, enhancing sustainability while maintaining consistent drying performance.
- Energy Efficiency - Heat pump dehydrators reduce electricity use by recycling heat during the drying cycle.
- Low Temperature Drying - Operates at lower temperatures, preventing nutrient loss and better retaining food quality.
- Cost-Effectiveness - Longer initial investment is offset by significant savings in energy bills over time.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Electric dehydrators typically consume more electricity, ranging from 300 to 600 watts, whereas heat pump dehydrators use advanced technology to reduce power consumption by up to 50%. This energy efficiency makes heat pump dehydrators a cost-effective choice for long-term meal prep.
Heat pump dehydrators operate at lower temperatures while maintaining drying quality, which significantly cuts energy use compared to traditional electric models. Their ability to recycle heat reduces waste, making them more environmentally friendly. Choosing a heat pump dehydrator can result in notable savings on electricity bills during frequent meal preparation cycles.
Drying Performance and Speed
Which offers better drying performance and speed for meal prep, an electric dehydrator or a heat pump dehydrator? Electric dehydrators typically provide faster drying times due to their direct heating elements, making them ideal for quick meal prep. Heat pump dehydrators, while slower, offer more energy-efficient drying with consistent temperature control, preserving nutrients and flavors more effectively.
Nutrient Retention and Food Quality
Electric dehydrators typically use steady heat to preserve food, but the higher temperatures can slightly reduce nutrient retention compared to heat pump dehydrators. Heat pump dehydrators operate at lower temperatures with efficient moisture removal, enhancing nutrient preservation and maintaining superior food texture and flavor.
- Electric dehydrators generate consistent heat - This can lead to minor nutrient loss due to higher temperature exposure during dehydration.
- Heat pump dehydrators use lower temperatures - The gentler drying process better preserves vitamins and antioxidants in meal prep ingredients.
- Heat pump technology maintains food quality - Improved moisture control results in better texture and flavor retention in dried foods.
Noise Levels and User Experience
Electric dehydrators typically generate higher noise levels due to continuous fan operation, which may affect user comfort during meal prep. Heat pump dehydrators operate more quietly and offer a more pleasant experience, especially in smaller kitchens.
- Electric Dehydrator Noise - Produces consistent fan noise, ranging from 50 to 60 decibels, which can be distracting in quiet environments.
- Heat Pump Dehydrator Noise - Runs at lower noise levels around 40 to 50 decibels, ensuring minimal disruption while drying food.
- User Experience - Heat pump models provide efficient dehydration with quieter operation, improving usability for extended meal prep sessions.
Choosing a heat pump dehydrator enhances meal preparation by delivering quieter performance and better user comfort.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Operating Expenses
Electric dehydrators typically have a lower initial cost, ranging from $40 to $200, making them more accessible for home meal prep. Their operating expenses are moderate, with power consumption averaging around 300 to 600 watts per hour, depending on the model and usage frequency.
Heat pump dehydrators, while more expensive upfront--often costing between $300 and $1,500--offer greater energy efficiency, consuming nearly 50% less electricity compared to electric models. Over time, the reduced operating costs due to lower energy usage can offset the higher initial investment, especially for frequent or large-scale meal preparation.
Suitability for Different Meal Prep Needs
Electric dehydrators offer precise temperature control and faster drying times, making them ideal for meal prep involving delicate fruits, herbs, and thinly sliced vegetables. Heat pump dehydrators provide energy-efficient dehydration with consistent low temperatures, suitable for preserving large quantities of meats and sturdier vegetables. Choosing between these depends on meal prep volume, ingredient type, and energy consumption preferences.
Related Important Terms
Low-temp dehydration efficiency
Electric dehydrators offer consistent low-temperature control ideal for preserving nutrients during meal prep, while heat pump dehydrators achieve higher energy efficiency by recycling heat but may have slower drying times at low temperatures. Selecting between the two depends on balancing precise temperature management with energy consumption for optimal low-temp dehydration performance.
Heat pump moisture recovery
Heat pump dehydrators excel in meal prep by efficiently recovering moisture through closed-loop systems, reducing energy consumption by up to 50% compared to electric dehydrators. This moisture recovery technology preserves food quality and accelerates drying times, making them ideal for consistent, large-batch dehydration.
Precision airflow mapping
Electric dehydrators feature consistent temperature controls and direct heating elements that provide reliable drying but may lack uniform airflow distribution, which can lead to uneven dehydration. Heat pump dehydrators utilize advanced precision airflow mapping technology to circulate air more evenly and efficiently, ensuring consistent moisture removal and superior preservation of meal prep ingredients.
Sequential batch dehydration
Electric dehydrators provide consistent temperatures ideal for sequential batch dehydration, ensuring uniform moisture removal in meal prep. Heat pump dehydrators offer energy-efficient drying with lower temperatures, preserving nutrient quality across multiple drying cycles.
Energy consumption per gram dried
Electric dehydrators typically consume 0.5 to 1.5 kWh per kilogram of food dried, resulting in moderate energy efficiency for meal prep. Heat pump dehydrators, however, operate at 0.3 to 0.8 kWh per kilogram, significantly reducing energy consumption and cost per gram dried while maintaining effective dehydration performance.
Retained phytonutrient index
Electric dehydrators typically preserve a higher Retained Phytonutrient Index by maintaining consistent low temperatures that minimize nutrient degradation during meal prep. Heat pump dehydrators, while energy-efficient, may cause greater nutrient loss due to fluctuating humidity and temperature levels affecting phytonutrient stability.
Hybrid-cycle food dehydration
Hybrid-cycle food dehydration combines the rapid drying efficiency of electric dehydrators with the energy-saving technology of heat pump systems, offering optimal moisture removal for meal prep. This method enhances nutrient retention and flavor preservation while reducing electricity consumption compared to traditional single-cycle dehydrators.
Volatile aroma preservation
Electric dehydrators use consistent low heat to effectively remove moisture while preserving the volatile aroma compounds essential for flavorful meal prep, ensuring better taste retention. Heat pump dehydrators operate at lower temperatures with controlled humidity, enhancing volatile aroma preservation by minimizing oxidation and nutrient loss during dehydration.
Smart humidity monitoring
Electric dehydrators typically offer precise temperature control but lack advanced smart humidity monitoring, which can affect optimal moisture removal during meal prep. Heat pump dehydrators integrate smart humidity sensors to adjust drying cycles automatically, ensuring consistent dehydration and preserving meal quality efficiently.
Electric dehydrator vs Heat pump dehydrator for meal prep. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com