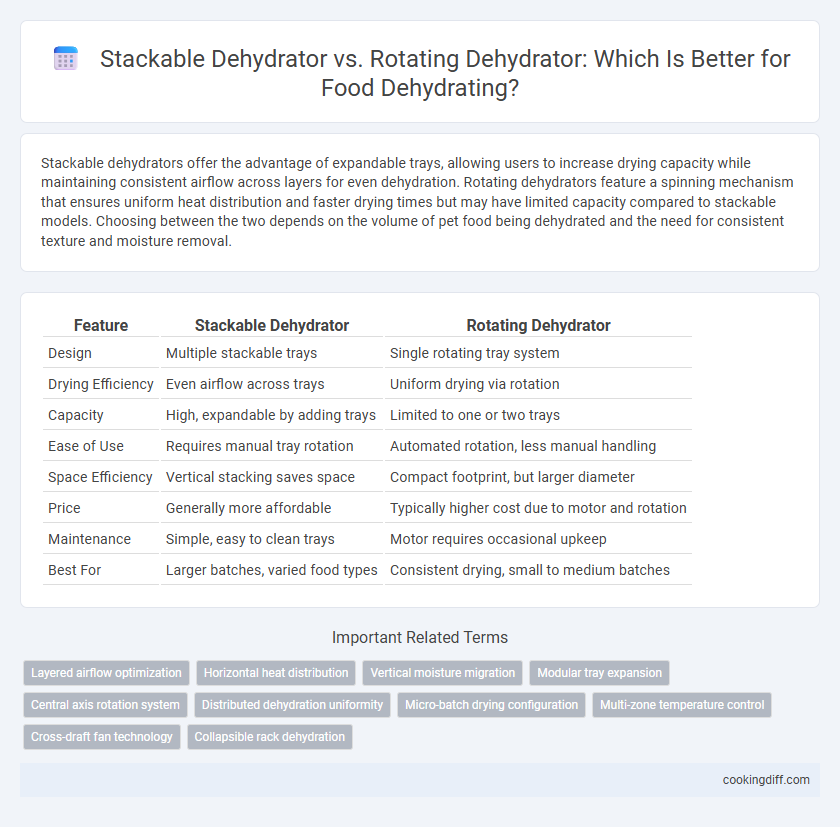
Stackable dehydrators offer the advantage of expandable trays, allowing users to increase drying capacity while maintaining consistent airflow across layers for even dehydration. Rotating dehydrators feature a spinning mechanism that ensures uniform heat distribution and faster drying times but may have limited capacity compared to stackable models. Choosing between the two depends on the volume of pet food being dehydrated and the need for consistent texture and moisture removal.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stackable Dehydrator | Rotating Dehydrator |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Multiple stackable trays | Single rotating tray system |
| Drying Efficiency | Even airflow across trays | Uniform drying via rotation |
| Capacity | High, expandable by adding trays | Limited to one or two trays |
| Ease of Use | Requires manual tray rotation | Automated rotation, less manual handling |
| Space Efficiency | Vertical stacking saves space | Compact footprint, but larger diameter |
| Price | Generally more affordable | Typically higher cost due to motor and rotation |
| Maintenance | Simple, easy to clean trays | Motor requires occasional upkeep |
| Best For | Larger batches, varied food types | Consistent drying, small to medium batches |
Introduction to Food Dehydration Methods
Food dehydration methods vary widely, with stackable and rotating dehydrators being two common types designed to preserve food by removing moisture. Stackable dehydrators consist of removable trays stacked vertically, while rotating dehydrators have a mechanism that circulates food trays for even drying.
- Stackable Dehydrators - Offer modular tray options for flexible drying quantities and are easy to clean.
- Rotating Dehydrators - Provide consistent airflow and uniform dehydration by continuously rotating trays.
- Drying Efficiency - Rotating dehydrators often reduce drying time due to better heat distribution compared to stackable models.
Choosing between stackable and rotating dehydrators depends on the volume of food and drying consistency required.
Overview: Stackable Dehydrator Design
Stackable dehydrators consist of multiple trays stacked vertically, allowing users to dry large quantities of food simultaneously while maintaining airflow between layers. This design promotes even dehydration by circulating warm air through each tray.
The compact vertical arrangement saves countertop space and offers flexibility to add or remove trays based on drying needs. Stackable dehydrators typically provide temperature control and timers, enhancing precision in the dehydration process.
Overview: Rotating Dehydrator Design
Rotating dehydrators feature a unique design where the trays rotate continuously inside the unit, ensuring even airflow distribution and consistent drying results. This mechanism reduces the need for manual tray rearrangement, enhancing efficiency during the dehydration process. Compared to stackable dehydrators, rotating models often provide more uniform dehydration, especially for fruits, vegetables, and herbs with varying moisture levels.
Drying Efficiency: Stackable vs Rotating Dehydrators
Stackable dehydrators offer consistent airflow through multiple trays, enhancing drying efficiency for larger batches. Rotating dehydrators improve heat distribution by moving trays, which can reduce drying times for unevenly arranged items.
- Airflow Design - Stackable dehydrators use vertical airflow to evenly dry food across all trays simultaneously.
- Heat Distribution - Rotating dehydrators continuously rotate trays to expose all surfaces to heat, minimizing hotspots.
- Batch Capacity - Stackable models handle larger quantities more efficiently due to their extended tray space.
Temperature Distribution Comparison
Stackable dehydrators provide consistent temperature distribution by allowing hot air to circulate evenly through fixed trays, ensuring uniform dehydration of all items. Rotating dehydrators, however, rely on the rotation mechanism to expose all sides to heat, which can lead to slight temperature variations across different layers.
Temperature distribution in stackable dehydrators is often more stable because each tray receives a direct airflow path, minimizing cold spots and preserving nutrient content. Rotating dehydrators may experience uneven heat exposure if rotation speed or air circulation is insufficient, potentially causing inconsistent drying times. Choosing between the two depends on the specific needs for uniformity and batch size in food dehydration.
Capacity and Scalability of Each Model
Stackable dehydrators offer significant scalability by allowing users to add or remove trays based on the volume of food being processed, making them highly adaptable for varying batch sizes. Their capacity is generally larger per unit, accommodating wide spreads of sliced fruits, vegetables, or meats simultaneously.
Rotating dehydrators feature a fixed capacity with trays that rotate around a central heat source, ensuring even drying but limiting scalability since the number of trays is fixed. These models are better suited for consistent, moderate-volume dehydration tasks with reliable airflow distribution.
Ease of Use and Maintenance
Which type of dehydrator is easier to use and maintain, stackable or rotating? Stackable dehydrators offer straightforward loading and unloading with removable trays, simplifying cleaning and maintenance. Rotating dehydrators require less manual rotation during use but often involve more complex parts, making upkeep more challenging.
Versatility for Different Foods
Stackable dehydrators offer superior versatility for drying a wide variety of foods simultaneously by allowing independent temperature and airflow control on each tray, ideal for dehydrating fruits, vegetables, and herbs at different rates. Rotating dehydrators provide consistent airflow and even drying by spinning the trays, but may be less flexible when handling foods that require distinct drying conditions. For users prioritizing multi-food customization, stackable models deliver greater adaptability in achieving optimal dehydration results.
Energy Consumption and Cost Analysis
Stackable dehydrators generally consume less energy per batch due to their modular design allowing selective tray usage, whereas rotating dehydrators use a consistent motor that can increase overall energy consumption. Cost analysis reveals that stackable models often have a lower initial price but may incur higher maintenance costs compared to the more durable rotating types.
- Energy efficiency - Stackable dehydrators enable energy savings by operating only necessary trays, reducing power use.
- Initial investment - Rotating dehydrators tend to have higher upfront costs due to integrated motor and mechanics.
- Maintenance expenses - Stackable units might require more frequent upkeep because of multiple detachable components.
Related Important Terms
Layered airflow optimization
Stackable dehydrators utilize layered airflow optimization by directing air vertically through stacked trays, ensuring even dehydration and preserving nutrient consistency across each layer. Rotating dehydrators enhance airflow distribution by continuously moving trays, preventing moisture pockets and promoting uniform drying efficiency.
Horizontal heat distribution
Stackable dehydrators provide horizontal heat distribution by allowing warm air to flow evenly through each tray, ensuring consistent dehydration of food across all layers. Rotating dehydrators sometimes experience uneven heat exposure as the trays move, which can lead to inconsistent drying results compared to the stable airflow in stackable models.
Vertical moisture migration
Stackable dehydrators promote efficient vertical moisture migration by allowing heat and air to flow consistently through multiple trays stacked vertically, ensuring even drying across all layers. In contrast, rotating dehydrators enhance uniform dehydration by continuously turning the trays, which redistributes moisture and prevents uneven drying hotspots.
Modular tray expansion
Stackable dehydrators offer modular tray expansion, allowing users to add or remove trays based on batch size for flexible drying capacity. Rotating dehydrators typically have fixed trays that rotate within a single unit, limiting the ability to easily increase drying space compared to stackable models.
Central axis rotation system
Stackable dehydrators utilize a stationary central axis with trays stacked vertically, promoting even airflow and temperature distribution, ideal for large batches. Rotating dehydrators feature a central axis that spins trays to enhance uniform drying by continually moving food closer to the heat source.
Distributed dehydration uniformity
Stackable dehydrators provide distributed dehydration uniformity by allowing even airflow through multiple layers, ensuring consistent drying across all trays. In contrast, rotating dehydrators achieve uniformity by mechanically turning the trays, promoting equal exposure to heat and airflow throughout the dehydration process.
Micro-batch drying configuration
Stackable dehydrators allow precise micro-batch drying by enabling separate trays to be controlled individually, optimizing airflow and temperature for varied food types. Rotating dehydrators provide uniform drying through continuous movement but may lack the flexibility needed for small, heterogeneous batches requiring tailored drying conditions.
Multi-zone temperature control
Stackable dehydrators provide precise multi-zone temperature control by allowing each tray to operate independently, ensuring uniform drying for different types of food simultaneously. Rotating dehydrators, while effective at circulating air, typically offer a single temperature setting, limiting flexibility for dehydrating items with varying moisture content.
Cross-draft fan technology
Stackable dehydrators using cross-draft fan technology circulate air horizontally through each tray, ensuring even dehydration and consistent moisture removal across all layers. Rotating dehydrators typically rely on a central fan with rotary motion, which can create uneven airflow and variable drying times compared to the uniform air distribution in stackable models.
Stackable dehydrator vs Rotating dehydrator for dehydrating. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com