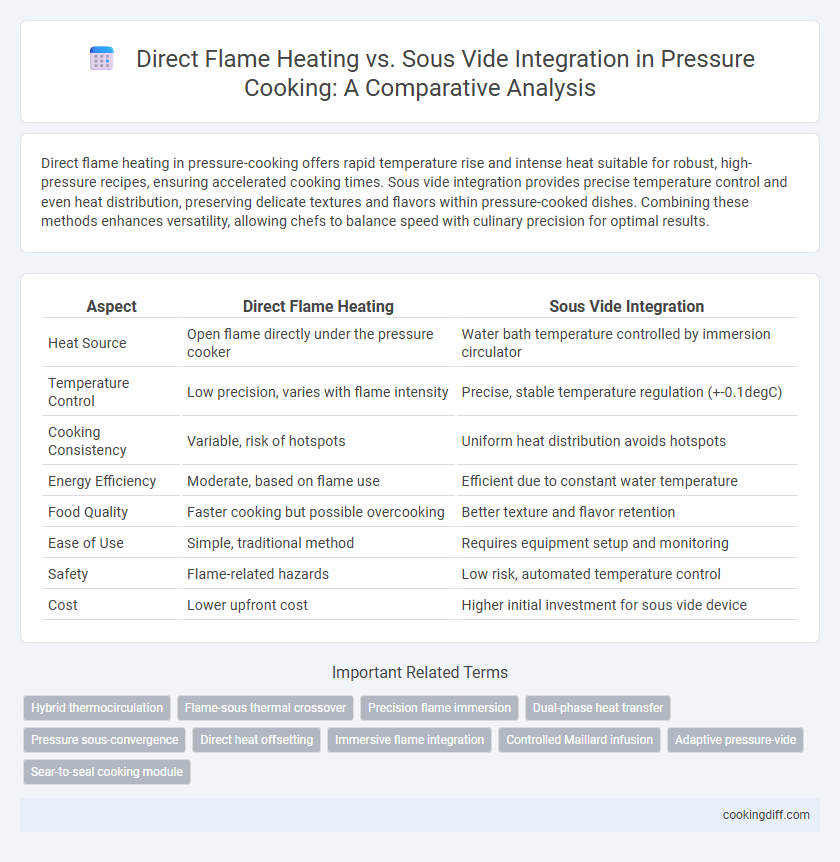
Direct flame heating in pressure-cooking offers rapid temperature rise and intense heat suitable for robust, high-pressure recipes, ensuring accelerated cooking times. Sous vide integration provides precise temperature control and even heat distribution, preserving delicate textures and flavors within pressure-cooked dishes. Combining these methods enhances versatility, allowing chefs to balance speed with culinary precision for optimal results.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Direct Flame Heating | Sous Vide Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | Open flame directly under the pressure cooker | Water bath temperature controlled by immersion circulator |
| Temperature Control | Low precision, varies with flame intensity | Precise, stable temperature regulation (+-0.1degC) |
| Cooking Consistency | Variable, risk of hotspots | Uniform heat distribution avoids hotspots |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate, based on flame use | Efficient due to constant water temperature |
| Food Quality | Faster cooking but possible overcooking | Better texture and flavor retention |
| Ease of Use | Simple, traditional method | Requires equipment setup and monitoring |
| Safety | Flame-related hazards | Low risk, automated temperature control |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher initial investment for sous vide device |
Introduction to Pressure-Cooking Methods
Pressure-cooking relies on high-pressure steam to rapidly cook food, intensifying flavors and tenderizing ingredients efficiently. Direct flame heating applies immediate heat to the pot, resulting in quicker pressure buildup and faster cooking times.
Sous vide integration with pressure-cooking combines precise temperature control and uniform heat distribution with the benefits of pressure-induced cooking. This hybrid method enhances texture and nutrient retention while maintaining safety and consistency in results.
Understanding Direct Flame Heating in Pressure-Cookers
Direct flame heating in pressure cookers involves placing the cookware directly on a gas stove flame, allowing rapid heat transfer and quick pressure buildup. This method demands durable materials like stainless steel or cast iron to withstand intense heat and ensure even cooking. Understanding flame control is essential for maintaining safe pressure levels and preventing food overcooking or cooker damage.
The Science Behind Sous Vide Integration with Pressure-Cookers
The science behind sous vide integration with pressure cookers lies in precise temperature control and consistent heat distribution, which enhances flavor infusion and nutrient retention. Direct flame heating provides rapid temperature changes but often lacks the stable environment required for sous vide techniques. Combining sous vide with pressure cooking ensures pressure-induced tenderization while maintaining exact water bath temperatures, optimizing the cooking process through molecular precision.
Heat Distribution: Direct Flame vs Sous Vide
Direct flame heating in pressure cooking offers rapid heat transfer by directly applying intense heat to the vessel's base, which can lead to uneven heat distribution and potential hotspots. This method requires constant monitoring to prevent scorching and ensures the pressure builds quickly for efficient cooking.
Sous vide integration provides precise and even heat distribution by circulating temperature-controlled water around the sealed cooking vessel, maintaining consistent thermal conditions. This gentle, uniform heat minimizes the risk of overcooking and preserves texture and flavor during pressure-cooking processes.
Cooking Precision and Temperature Control Compared
Direct flame heating in pressure cooking offers rapid heat-up and strong temperature intensity but often lacks the precise temperature control achieved through sous vide integration. Sous vide combined with pressure cooking enables a consistent, controlled cooking environment, enhancing precision in temperature management for optimal food texture and safety.
- Direct flame heating provides high heat intensity - It quickly raises the pressure cooker to high temperatures, ideal for fast cooking but with less consistent temperature stability.
- Sous vide integration allows exact temperature control - This technique maintains a precise water bath temperature, improving cooking accuracy and reducing the risk of overcooking.
- Cooking precision is enhanced with sous vide pressure cooking - The precise thermal regulation ensures uniform doneness and better retention of flavors and nutrients.
Impact on Food Texture and Flavor Profiles
Direct flame heating in pressure cooking intensifies Maillard reactions, enhancing browning and deepening flavor complexity, while sous vide integration yields more uniform texture and precise flavor infusion by controlling temperature gradually. Texture from direct flame can be less consistent, often firmer or tougher, as rapid heat impacts connective tissues differently compared to the gentle, controlled heat of sous vide.
- Direct flame heating accelerates caramelization - This method boosts rich, robust flavors but may create uneven textures due to rapid temperature changes.
- Sous vide integration ensures uniform cooking - It preserves tenderness and delicate flavors by maintaining precise temperature control.
- Flavor profiles diverge significantly - Direct flame emphasizes smoky, intense notes, whereas sous vide highlights natural, subtle tastes of ingredients.
Energy Efficiency: Which Method Saves More?
Direct flame heating in pressure-cooking typically consumes more energy due to heat loss and constant temperature fluctuations. Sous vide integration allows precise temperature control, reducing energy waste and improving overall cooking efficiency.
- Direct Flame Heating Energy Loss - Heat escapes easily into the environment, increasing fuel consumption.
- Sous Vide Precision - Maintains consistent temperature with minimal energy input.
- Energy Savings - Sous vide paired with pressure-cooking optimizes energy use by minimizing overcooking and reheating.
Sous vide integration is the more energy-efficient method for pressure-cooking compared to direct flame heating.
Safety Considerations in Direct Flame and Sous Vide Pressure-Cooking
Direct flame heating in pressure-cooking requires robust safety mechanisms such as flame failure devices and pressure release valves to prevent accidents. Sous vide integration minimizes high-pressure risks by maintaining precise temperature control in water baths, reducing the likelihood of pressure-related hazards.
Pressure cookers using direct flame are more susceptible to uneven heating and potential pressure build-up, which necessitates constant monitoring and adherence to manufacturer safety guidelines. Sous vide pressure-cooking offers enhanced safety through consistent temperature regulation and reduced pressure fluctuations. Both methods demand proper equipment maintenance to ensure reliable safety performance during operation.
Versatility and Recipe Compatibility
| Direct flame heating offers rapid temperature increase and is ideal for traditional pressure-cooking recipes requiring intense heat and quick pressure buildup. Sous vide integration enhances versatility by enabling precise temperature control and gentle cooking, allowing a broader range of recipes involving delicate proteins and vegetables to be pressure-cooked effectively. Combining these methods expands recipe compatibility, catering to both quick-cook meals and long-duration infusions under pressure. |
Related Important Terms
Hybrid thermocirculation
Hybrid thermocirculation combines direct flame heating and sous vide integration to optimize pressure-cooking by ensuring precise temperature control and even heat distribution. This method enhances cooking efficiency, texture, and flavor retention while reducing cooking time compared to traditional direct flame pressure cookers.
Flame-sous thermal crossover
Pressure-cooking with direct flame heating offers rapid, high-intensity thermal transfer ideal for traditional recipes, while sous vide integration ensures precise, consistent temperature control by combining low-temperature water baths with pressure environments. The flame-sous thermal crossover enhances cooking versatility, allowing chefs to achieve both quick searing and slow, even heat penetration within a single pressure-cooking system.
Precision flame immersion
Direct flame heating in pressure-cooking offers rapid temperature elevation and intense heat control but may lack the precise temperature stability essential for sous vide integration, which relies on consistent, low-temperature immersion for optimal cooking results. Precision flame immersion technology advances traditional methods by combining exact flame modulation with controlled water immersion, enhancing flavor infusion and texture retention while minimizing overcooking risks.
Dual-phase heat transfer
Direct flame heating in pressure cooking utilizes conduction and convection to rapidly increase temperature and pressure, enabling quick heat transfer through direct contact and steam circulation. Sous vide integration introduces precise, controlled water bath temperatures, combining convective heat transfer with gentle, uniform heat application, optimizing the dual-phase heat transfer process for enhanced texture and nutrient retention.
Pressure sous-convergence
Pressure sous-convergence combines direct flame heating's rapid temperature increase with sous vide's precise temperature control, optimizing pressure-cooking efficiency and food texture. This integration ensures consistent heat distribution, enhances flavor infusion, and reduces cooking time compared to traditional methods.
Direct heat offsetting
Direct flame heating in pressure cooking delivers rapid, intense heat transfer that accelerates cooking times but risks uneven heat distribution and potential burning. Sous vide integration ensures precise temperature control and uniform heat, offsetting the drawbacks of direct flame by maintaining consistent internal pressure and preventing overheating.
Immersive flame integration
Immersive flame integration in pressure-cooking enhances heat transfer efficiency and flavor development by directly applying intense, controlled heat to the cooking vessel, unlike sous vide methods that rely on precise water bath temperatures for even cooking without browning. This technique optimizes Maillard reactions and reduces cooking time, offering a unique blend of traditional flame intensity with modern pressure-cooking technology.
Controlled Maillard infusion
Direct flame heating in pressure-cooking enhances Maillard reactions by rapidly reaching high temperatures, creating intense browning and rich flavor infusion, whereas sous vide integration offers precise temperature control that limits Maillard development but ensures uniform cooking and moisture retention. Optimizing controlled Maillard infusion requires balancing direct flame's high heat benefits with sous vide's consistent thermal regulation for improved texture and flavor complexity.
Adaptive pressure-vide
Adaptive pressure-vide technology seamlessly combines direct flame heating with sous vide precision, enabling consistent temperature control and enhanced flavor infusion during pressure-cooking. This hybrid method optimizes cooking efficiency by preserving nutrients and textures, outperforming traditional direct flame or sous vide techniques alone.
Direct flame heating vs sous vide integration for pressure-cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com