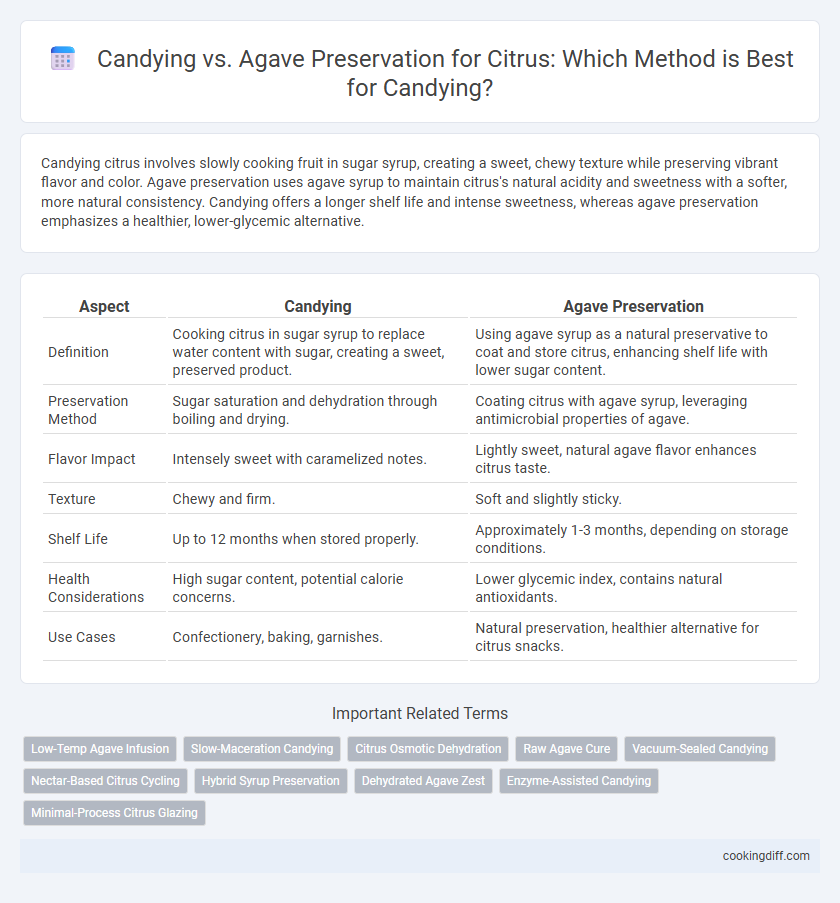
Candying citrus involves slowly cooking fruit in sugar syrup, creating a sweet, chewy texture while preserving vibrant flavor and color. Agave preservation uses agave syrup to maintain citrus's natural acidity and sweetness with a softer, more natural consistency. Candying offers a longer shelf life and intense sweetness, whereas agave preservation emphasizes a healthier, lower-glycemic alternative.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Candying | Agave Preservation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cooking citrus in sugar syrup to replace water content with sugar, creating a sweet, preserved product. | Using agave syrup as a natural preservative to coat and store citrus, enhancing shelf life with lower sugar content. |
| Preservation Method | Sugar saturation and dehydration through boiling and drying. | Coating citrus with agave syrup, leveraging antimicrobial properties of agave. |
| Flavor Impact | Intensely sweet with caramelized notes. | Lightly sweet, natural agave flavor enhances citrus taste. |
| Texture | Chewy and firm. | Soft and slightly sticky. |
| Shelf Life | Up to 12 months when stored properly. | Approximately 1-3 months, depending on storage conditions. |
| Health Considerations | High sugar content, potential calorie concerns. | Lower glycemic index, contains natural antioxidants. |
| Use Cases | Confectionery, baking, garnishes. | Natural preservation, healthier alternative for citrus snacks. |
Introduction to Citrus Preservation Methods
Candying and agave preservation are two effective methods for extending the shelf life of citrus fruits by enhancing flavor and texture. Both techniques utilize natural sugars to inhibit microbial growth, but they differ in application and resulting taste profiles.
- Candying - Preserves citrus by soaking fruit slices in sugar syrup, creating a sweet, translucent glaze that intensifies natural citrus flavors.
- Agave Preservation - Involves submerging citrus in agave nectar, providing a subtly sweet and more natural preservation that retains juiciness.
- Flavor and Texture Impact - Candying yields a firmer, sugary coating, while agave preservation maintains a softer, more succulent texture with less added sweetness.
Understanding Candying: The Traditional Technique
Candying is a traditional preservation technique that involves slowly cooking citrus peels in a sugar syrup until they become translucent and infused with sweetness. This method enhances the natural flavor and texture of the fruit while creating a long-lasting product ideal for desserts and garnishes. Unlike agave preservation, candying relies on concentrated sugar to inhibit microbial growth, ensuring prolonged shelf life without altering the citrus's distinctive taste.
What is Agave Preservation?
What is agave preservation in the context of citrus fruits? Agave preservation involves using agave syrup as a natural sweetener and preservative to maintain the fruit's freshness and enhance flavor without relying on traditional sugar syrup. This method retains more nutrients and provides a distinct, mild sweetness compared to conventional candying techniques.
Key Differences: Candying vs Agave Preservation
Candying citrus involves infusing fruit peel with sugar syrup to create a sweet, translucent preserve, while agave preservation uses agave nectar as a natural sweetener to maintain fruit texture and enhance flavor. Both methods extend shelf life but differ significantly in ingredients, sweetness level, and texture outcomes.
- Sweetener Type - Candying relies on granulated sugar, whereas agave preservation uses agave nectar, a natural low-glycemic sweetener.
- Texture Result - Candying yields a chewy, crystallized texture, while agave preservation maintains a softer, more natural fruit consistency.
- Flavor Impact - Candying imparts a strong sugary taste, whereas agave offers a milder, caramel-like sweetness that complements citrus flavors.
Choosing between candying and agave preservation depends on desired sweetness, texture, and natural ingredient preferences.
Flavor Profiles: Citrus in Candying vs Agave Methods
Candying citrus involves simmering fruit in a sugar syrup, enhancing its natural sweetness and intensifying the bright, tangy notes characteristic of citrus flavors. This method preserves the vibrant, zesty aroma and delivers a rich, sugary finish that accentuates the fruit's inherent citrus complexity.
Agave preservation imparts a distinct earthy sweetness to citrus, blending the fruit's natural acidity with the mellow, caramel-like undertones of agave nectar. This technique produces a softer, less syrupy texture compared to traditional candying, allowing the citrus's bright citrus oils to remain prominent. The result is a balanced flavor profile combining tropical sweetness with a subtle floral depth unique to agave preservation.
Impact on Texture: Comparing Preserved Citrus
| Preservation Method | Impact on Texture | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Candying | Firm and Chewy | Candying preserves citrus by infusing sugar into the peel and flesh, resulting in a dense, chewy texture while maintaining structural integrity of the fruit segments. |
| Agave Preservation | Soft and Moist | Agave syrup infusion retains more moisture in the citrus, leading to a softer texture but with less firmness compared to traditional candying methods. |
Health and Nutritional Considerations
Candying citrus involves coating fruit in sugar syrup which significantly increases calorie content and may raise blood glucose levels. Agave preservation uses agave nectar, a natural sweetener with a lower glycemic index, providing a potentially healthier alternative for maintaining citrus.
- Candying increases sugar content - This method adds substantial refined sugar, impacting overall calorie intake and blood sugar spikes.
- Agave nectar offers a lower glycemic impact - Its natural fructose content leads to slower glucose absorption compared to traditional candying.
- Both methods affect nutrient retention differently - Candying can reduce vitamin levels due to heat exposure, while agave preservation tends to retain more nutrients.
Culinary Uses for Candied and Agave-Preserved Citrus
Candied citrus zest offers a rich, sweet flavor and a chewy texture ideal for garnishing desserts, enhancing pastries, and adding complexity to cocktails. Agave-preserved citrus retains a bright, tangy profile with a syrupy finish, making it perfect for glazing meats, sweetening beverages, and complementing cheese boards.
Chefs prefer candied citrus for its long shelf life and concentrated sweetness that elevates baked goods and confections. Agave-preserved citrus is favored for its natural sweetness and moisture, enhancing fresh dishes and creating balanced sweet-savory pairings in culinary applications.
Storage and Shelf Life Comparison
Candied citrus preserves for extended periods by fully saturating the fruit with sugar, which acts as a natural preservative to inhibit microbial growth, providing a shelf life that can exceed one year when stored in airtight containers at cool temperatures. This method maintains the citrus's texture and flavor more effectively compared to agave preservation, which relies on syrup infusion rather than full sugar saturation.
Agave preservation offers a shorter shelf life, typically up to six months, as the lower sugar concentration in agave syrup is less effective at preventing spoilage over time. The higher fructose content in agave syrup can lead to quicker fermentation and texture softening, making it less ideal for long-term storage of citrus fruits compared to traditional candying methods.
Related Important Terms
Low-Temp Agave Infusion
Low-temp agave infusion preserves citrus by slowly integrating natural sugars, maintaining texture and enhancing flavor without the high heat damage typical of candying. This method retains higher vitamin C content and delivers a balanced sweetness, making it a superior preservation technique compared to traditional candying for citrus fruits.
Slow-Maceration Candying
Slow-maceration candying preserves the natural citrus flavors by gradually infusing sugar over several weeks, maintaining the fruit's texture and enhancing its sweetness without overpowering acidity. This method contrasts with agave preservation, which relies on agave syrup's distinct flavor and higher fructose content, offering a quicker but less nuanced sweetening process.
Citrus Osmotic Dehydration
Citrus osmotic dehydration in candying involves immersing fruit peels in concentrated sugar solutions, facilitating water removal while infusing sweetness without heat damage, preserving texture and flavor. Agave preservation uses agave syrup as an osmotic agent, offering a natural alternative that enhances antioxidant retention but may alter citrus sweetness profiles compared to traditional candying methods.
Raw Agave Cure
Raw agave cure preserves citrus by infusing natural sugars and enzymes that enhance flavor while maintaining a tender texture, unlike traditional candying which relies on prolonged boiling in sugar syrup. This method improves shelf life organically and retains nutrients better compared to agave-based preservation techniques that often involve higher heat and processing.
Vacuum-Sealed Candying
Vacuum-sealed candying preserves citrus by removing air and locking in flavors, which significantly enhances shelf life and maintains vibrant texture compared to agave preservation that relies on sugar infusion for sweetness and moisture retention. This method prevents oxidation and microbial growth more effectively, resulting in citrus peels that remain flavorful and visually appealing without the added sugars found in agave preservation.
Nectar-Based Citrus Cycling
Nectar-based citrus cycling in candying preserves the fruit's natural sweetness by gradually replacing water content with sugar syrup, enhancing flavor and texture without fermentation risks. Agave preservation, while effective for extending shelf life, introduces distinct flavor profiles and less concentrated sugar infusion, making candying preferable for maintaining authentic citrus essence.
Hybrid Syrup Preservation
Hybrid syrup preservation combines the concentrated sweetness of agave with the traditional candying process to enhance citrus shelf life and flavor retention. This method maintains the vibrant citrus peel texture while offering a natural, less processed alternative to conventional sugar candying techniques, optimizing both taste and nutritional value.
Dehydrated Agave Zest
Dehydrated agave zest offers a unique preservation method for citrus, maintaining vibrant flavor and natural sugars without the heavy syrup saturation typical in candying. Unlike traditional candying, agave preservation enhances citrus zest's fruity notes while providing a lower glycemic alternative, ideal for health-conscious applications.
Enzyme-Assisted Candying
Enzyme-assisted candying enhances the preservation of citrus by using pectinase and cellulase enzymes to break down cell walls, facilitating sugar penetration and improved texture compared to traditional agave preservation, which relies on natural sugars and slower dehydration. This method accelerates syrup absorption, maintains vibrant color, and increases shelf life, making enzyme-assisted candying a more efficient and consistent process for citrus preservation.
Candying vs Agave Preservation for citrus. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com